Pemphigus vulgaris immunoglobulin G can recognize a 130 000 MW antigen other than desmoglein 3 on peripheral blood mononuclear cell surface
- PMID: 17386081
- PMCID: PMC2265957
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2567.2007.02585.x
Pemphigus vulgaris immunoglobulin G can recognize a 130 000 MW antigen other than desmoglein 3 on peripheral blood mononuclear cell surface
Abstract
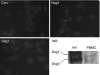
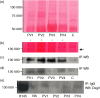
Pemphigus vulgaris (PV) is considered to be an autoimmune disease affecting skin and mucous membranes. Traditionally, PV autoantibodies are thought to recognize antigens located in the intercellular substance (ICS) of keratinocytes; antigens represented mainly by the desmosomal cadherin desmoglein 3 (Dsg3). Accordingly, titres of anti-ICS and anti-Dsg3 immunoglobulin G (IgG) are considered to be major laboratory criteria when making a diagnosis of PV. In this paper, we demonstrated for the first time that PV IgG bind antigen(s) expressed on the surface of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC), as revealed by immunofluorescence studies. This novel autoantigen is immunoprecipitated by PV IgG as a 130 000 molecular weight protein. However, Western blot analysis of the immunocomplexes failed to show reactivity with anti-Dsg3 monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies. Taken together, our data provide strong evidence that PV autoimmunity targets a 130 000 antigen other than Dsg3 on PBMC. This shifting from epidermis to blood cells may open new perspectives for a better understanding of pemphigus autoimmunity and more rational approaches to its treatment.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Binding of pemphigus vulgaris IgG to antigens in desmosome core domains excludes immune complexes rather than directly splitting desmosomes.Br J Dermatol. 2010 May;162(5):1049-55. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.2010.09672.x. Epub 2010 Mar 4. Br J Dermatol. 2010. PMID: 20222919
-
Pathogenic IgG antibodies against desmoglein 3 in pemphigus vulgaris are regulated by HLA-DRB1*04:02-restricted T cells.J Immunol. 2014 Nov 1;193(9):4391-9. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1401081. Epub 2014 Sep 24. J Immunol. 2014. PMID: 25252957
-
Pemphigus vulgaris-IgG causes a rapid depletion of desmoglein 3 (Dsg3) from the Triton X-100 soluble pools, leading to the formation of Dsg3-depleted desmosomes in a human squamous carcinoma cell line, DJM-1 cells.J Invest Dermatol. 1999 Jan;112(1):67-71. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1747.1999.00463.x. J Invest Dermatol. 1999. PMID: 9886266
-
Pemphigus vulgaris: recent advances in our understanding of its pathogenesis.Minerva Stomatol. 2007 Apr;56(4):215-23. Minerva Stomatol. 2007. PMID: 17452959 Review. English, Italian.
-
Pemphigus: a Comprehensive Review on Pathogenesis, Clinical Presentation and Novel Therapeutic Approaches.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018 Feb;54(1):1-25. doi: 10.1007/s12016-017-8662-z. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2018. PMID: 29313220 Review.
Cited by
-
An Investigation on Micro-Raman Spectra and Wavelet Data Analysis for Pemphigus Vulgaris Follow-up Monitoring.Sensors (Basel). 2008 Jun 1;8(6):3656-3664. doi: 10.3390/s8063656. Sensors (Basel). 2008. PMID: 27879899 Free PMC article.
-
Senescent cancer-associated fibroblasts secrete active MMP-2 that promotes keratinocyte dis-cohesion and invasion.Br J Cancer. 2014 Sep 9;111(6):1230-7. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2014.438. Epub 2014 Aug 12. Br J Cancer. 2014. PMID: 25117810 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of the cancer-associated glucocorticoid system: key role of 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2.Br J Cancer. 2017 Sep 26;117(7):984-993. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2017.243. Epub 2017 Aug 10. Br J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28797028 Free PMC article.
-
Desmosomal interactome in keratinocytes: a systems biology approach leading to an understanding of the pathogenesis of skin disease.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009 Nov;66(21):3517-33. doi: 10.1007/s00018-009-0139-7. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2009. PMID: 19756386 Free PMC article.
-
Pemphigus autoimmunity: hypotheses and realities.Autoimmunity. 2012 Feb;45(1):7-35. doi: 10.3109/08916934.2011.606444. Epub 2011 Sep 23. Autoimmunity. 2012. PMID: 21939410 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bystryn JC, Rudolph JL. Pemphigus Lancet. 2005;366:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Wolff K, Schreiner E. Ultrastructural localization of pemphigus autoantibodies within the epidermis. Nature. 1971;229:59–61. - PubMed
-
- Amagai M, Klaus-Kovtun V, Stanley JR. Autoantibodies against a novel epithelial cadherin in pemphigus vulgaris, a disease of cell adhesion. Cell. 1991;67:869–77. - PubMed
-
- Dmochowski M, Hashimoto T, Garrod DR, Nishikawa T. Desmocollins I and II are recognized by certain sera from patients with various types of pemphigus particularly Brazilian pemphigus foliaceus. J Invest Dermatol. 1993;100:380–4. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

