Evaluation of two formulations of adjuvanted RTS, S malaria vaccine in children aged 3 to 5 years living in a malaria-endemic region of Mozambique: a Phase I/IIb randomized double-blind bridging trial
- PMID: 17386091
- PMCID: PMC1847838
- DOI: 10.1186/1745-6215-8-11
Evaluation of two formulations of adjuvanted RTS, S malaria vaccine in children aged 3 to 5 years living in a malaria-endemic region of Mozambique: a Phase I/IIb randomized double-blind bridging trial
Abstract
Background: Previous trials of the RTS, S malaria candidate vaccine have shown that this vaccine is safe, tolerated and immunogenic. The development plan for this vaccine aims at administering it in the first year of life through the Expanded Program on Immunization (EPI). The objective was to evaluate the safety and reactogenicity of RTS, S/AS02D (0.5 ml dose), a pediatric formulation of GlaxoSmithKline Biologicals' current malaria candidate vaccine RTS, S/AS02A (0.25 ml dose). A 0.5 ml dose of AS02D is composed of the same active ingredients in the same quantities as in a 0.25 ml dose of AS02A and has been developed to be easily introduced into routine EPI practices.
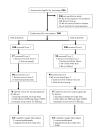
Methods: We performed a phase I/IIb randomized double-blind bridging study in a malaria-endemic region of Mozambique, to compare the safety and immunogenicity of both candidate vaccines with the aim of replacing RTS, S/AS02A with RTS, S/AS02D as the candidate pediatric vaccine. 200 Mozambican children aged 3 to 5 years were randomized 1:1 to receive one of the 2 vaccines according to a 0, 1, 2 month schedule.
Results: Both vaccines were safe and had similar reactogenicity profiles. All subjects with paired pre and post-vaccination samples showed a vaccine response with respect to anti-circumsporozoite (CS) antibodies irrespective of initial anti-CS serostatus. Geometric mean titers (GMTs) were 191 EU/ml (95% CI 150-242) in recipients of RTS, S/AS02D compared to 180 EU/ml (95% CI 146-221) in recipients of RTS, S/AS02A. For the anti-hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg), all subjects were seroprotected at day 90, and the GMTs were 23,978 mIU/ml (95% CI 17,896-32,127) in RTS, S/AS02D recipients and 17,410 mIU/ml (95% CI 13,322-22,752) in RTS, S/AS02A recipients. There was a decrease in anti-CS GMTs between months 3 and 14 in both groups (191 vs 22 EU/mL in RTS, S/AS02D group and 180 vs 29 EU/mL in RTS, S/AS02A group).
Conclusion: Our data show that the RTS, S/AS02D is safe, well tolerated, and demonstrates non-inferiority (defined as upper limit of the 95% confidence interval of the anti-CS GMT ratio of RTS, S/AS02A to RTS, S/AS02D below 3.0) of the antibody responses to circumsporozoite and HBsAg induced by the RTS, S/AS02D as compared to the RTS, S/AS02A.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Safety and immunogenicity of the RTS,S/AS02A candidate malaria vaccine in children aged 1-4 in Mozambique.Trop Med Int Health. 2007 Jan;12(1):37-46. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2006.01754.x. Trop Med Int Health. 2007. PMID: 17207146 Clinical Trial.
-
Safety of the RTS,S/AS02A malaria vaccine in Mozambican children during a Phase IIb trial.Vaccine. 2008 Jan 10;26(2):174-84. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2007.11.003. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Vaccine. 2008. PMID: 18069097 Clinical Trial.
-
Randomized, double-blind, phase 2a trial of falciparum malaria vaccines RTS,S/AS01B and RTS,S/AS02A in malaria-naive adults: safety, efficacy, and immunologic associates of protection.J Infect Dis. 2009 Aug 1;200(3):337-46. doi: 10.1086/600120. J Infect Dis. 2009. PMID: 19569965 Clinical Trial.
-
Towards an RTS,S-based, multi-stage, multi-antigen vaccine against falciparum malaria: progress at the Walter Reed Army Institute of Research.Vaccine. 2005 Mar 18;23(17-18):2243-50. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.01.142. Vaccine. 2005. PMID: 15755604 Review.
-
RTS,S/AS02A for malaria.Expert Rev Vaccines. 2006 Oct;5(5):611-5. doi: 10.1586/14760584.5.5.611. Expert Rev Vaccines. 2006. PMID: 17181435 Review.
Cited by
-
Plasmodium falciparum-specific cellular immune responses after immunization with the RTS,S/AS02D candidate malaria vaccine in infants living in an area of high endemicity in Mozambique.Infect Immun. 2009 Oct;77(10):4502-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00442-09. Epub 2009 Aug 3. Infect Immun. 2009. PMID: 19651872 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Correlations between three ELISA protocols measurements of RTS,S/AS01-induced anti-CSP IgG antibodies.PLoS One. 2023 May 23;18(5):e0286117. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0286117. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37220123 Free PMC article.
-
Flow Cytometry Based Detection and Isolation of Plasmodium falciparum Liver Stages In Vitro.PLoS One. 2015 Jun 12;10(6):e0129623. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0129623. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26070149 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of RTS,S/AS01E malaria vaccine and exploratory analysis on anti-circumsporozoite antibody titres and protection in children aged 5-17 months in Kenya and Tanzania: a randomised controlled trial.Lancet Infect Dis. 2011 Feb;11(2):102-9. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(10)70262-0. Epub 2011 Jan 13. Lancet Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21237715 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Why functional pre-erythrocytic and bloodstage malaria vaccines fail: a meta-analysis of fully protective immunizations and novel immunological model.PLoS One. 2010 May 19;5(5):e10685. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010685. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20502667 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Breman JG. The ears of the hippopotamus: manifestations, determinants, and estimates of the malaria burden. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64:1–11. - PubMed
-
- Gallup JL, Sachs JD. The economic burden of malaria. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2001;64:85–96. - PubMed
-
- Bojang KA, Olodude F, Pinder M, Ofori-Anyinam O, Vigneron L, Fitzpatrick S, Njie F, Kassanga A, Leach A, Milman J, Rabinovich R, McAdam KP, Kester KE, Heppner DG, Cohen JD, Tornieporth N, Milligan PJ. Safety and immunogenicty of RTS,S/AS02A candidate malaria vaccine in Gambian children. Vaccine. 2005;23:4148–4157. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2005.03.019. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources