Genome mapping and expression analyses of human intronic noncoding RNAs reveal tissue-specific patterns and enrichment in genes related to regulation of transcription
- PMID: 17386095
- PMCID: PMC1868932
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-3-r43
Genome mapping and expression analyses of human intronic noncoding RNAs reveal tissue-specific patterns and enrichment in genes related to regulation of transcription
Abstract
Background: RNAs transcribed from intronic regions of genes are involved in a number of processes related to post-transcriptional control of gene expression. However, the complement of human genes in which introns are transcribed, and the number of intronic transcriptional units and their tissue expression patterns are not known.
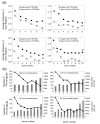
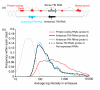
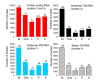
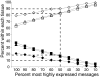
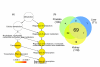
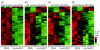
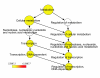
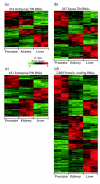
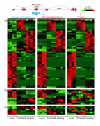
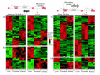
Results: A survey of mRNA and EST public databases revealed more than 55,000 totally intronic noncoding (TIN) RNAs transcribed from the introns of 74% of all unique RefSeq genes. Guided by this information, we designed an oligoarray platform containing sense and antisense probes for each of 7,135 randomly selected TIN transcripts plus the corresponding protein-coding genes. We identified exonic and intronic tissue-specific expression signatures for human liver, prostate and kidney. The most highly expressed antisense TIN RNAs were transcribed from introns of protein-coding genes significantly enriched (p = 0.002 to 0.022) in the 'Regulation of transcription' Gene Ontology category. RNA polymerase II inhibition resulted in increased expression of a fraction of intronic RNAs in cell cultures, suggesting that other RNA polymerases may be involved in their biosynthesis. Members of a subset of intronic and protein-coding signatures transcribed from the same genomic loci have correlated expression patterns, suggesting that intronic RNAs regulate the abundance or the pattern of exon usage in protein-coding messages.
Conclusion: We have identified diverse intronic RNA expression patterns, pointing to distinct regulatory roles. This gene-oriented approach, using a combined intron-exon oligoarray, should permit further comparative analysis of intronic transcription under various physiological and pathological conditions, thus advancing current knowledge about the biological functions of these noncoding RNAs.
Figures

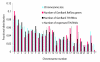
References
-
- Reis EM, Ojopi EP, Alberto FL, Rahal P, Tsukumo F, Mancini UM, Guimaraes GS, Thompson GM, Camacho C, Miracca E. et al.Large-scale transcriptome analyses reveal new genetic marker candidates of head, neck, and thyroid cancer. Cancer Res. 2005;65:1693–1699. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-3506. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

