Ultrasound guided dry needling and autologous blood injection for patellar tendinosis
- PMID: 17387140
- PMCID: PMC2465422
- DOI: 10.1136/bjsm.2006.034686
Ultrasound guided dry needling and autologous blood injection for patellar tendinosis
Abstract
Objective: To evaluate the efficacy of ultrasound guided dry needling and autologous blood injection for the treatment of patellar tendinosis.
Design: Prospective cohort study.
Setting: Hospital/clinic based.
Patients: 47 knees in 44 patients (40 men, 7 women, mean age 34.5 years, age range 17 to 54 years) with refractory tendinosis underwent sonographic examination of the patellar tendon following referral with a clinical diagnosis of patellar tendinosis (mean symptom duration 12.9 months).
Interventions: Ultrasound guided dry needling and injection of autologous blood into the site of patellar tendinosis was performed on two occasions four weeks apart.
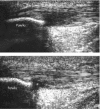
Main outcome measures: Pre- and post-procedure Victorian Institute of Sport Assessment scores (VISA) were collected to assess patient response to treatment. Follow up ultrasound examination was done in 21 patients (22 knees).
Results: Therapeutic intervention led to a significant improvement in VISA score: mean pre-procedure score = 39.8 (range 8 to 72) v mean post procedure score = 74.3 (range 29 to 100), p<0.001; mean follow up 14.8 months (range 6 to 22 months). Patients were able to return to their sporting interests. Follow up sonographic assessment showed a reduction in overall tendon thickness and in the size of the area of tendinosis (hypoechoic/anechoic areas within the proximal patellar tendon). A reduction was identified in interstitial tears within the tendon substance. Neovascularity did not reduce significantly or even increased.
Conclusions: Dry needling and autologous blood injection under ultrasound guidance shows promise as a treatment for patients with patellar tendinosis.
References
-
- Alfredson H. The chronic painful Achilles and patellar tendon: research on basic biology and treatment. Scand J Med Sci Sports 200515252–259. - PubMed
-
- Sharma P, Maffulli N. Tendon injury and tendinopathy: healing and repair. J Bone Joint Surg Am 200587187–202. - PubMed
-
- Alfredson H, Ohberg L. Neovascularisation in chronic painful patellar tendinosis‐promising results after sclerosing neovessels outside the tendon challenge the need for surgery. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc 20051374–80. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous