Inhibition of DAT function attenuates manganese accumulation in the globus pallidus
- PMID: 17387379
- PMCID: PMC1832113
- DOI: 10.1016/j.etap.2006.08.006
Inhibition of DAT function attenuates manganese accumulation in the globus pallidus
Abstract
Manganese (Mn) is an essential nutrient, though exposure to high concentrations may result in neurotoxicity characterized by alterations in dopamine neurobiology. To date, it remains elusive how and why Mn targets dopaminergic neurons although recently the role of the dopamine transporter has been suggested. Our primary goal of this study was to examine the potential roles of the monoamine transporters, dopamine transporter (DAT), serotonin transporter (SERT) and norepinephrine transporter (NET), in neuronal Mn transport. Using striatal synaptosomes, we found that only inhibition of DAT significantly decreased Mn accumulation. Furthermore, weanling rats chronically exposed to Mn, significantly accumulated Mn in several brain regions. However, rats receiving the specific DAT inhibitor GBR12909 (1 mg/kg bw, three times/week; four weeks) had significantly lower Mn levels only in the globus pallidus compared to saline-treated rats (p<0.05). Our data show that inhibition of DAT exclusively inhibits Mn accumulation in the globus pallidus during chronic exposure.
Figures


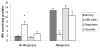
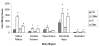

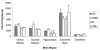
References
-
- Aschner M, Erikson KM, Dorman DC. Manganese dosimetry: species differences and implications for neurotoxicity. Crit Rev Tox. 2005;35:1–32. - PubMed
-
- Autissier N, Rochette L, Dumas P, Beley A, Loireau A, Bralet J. Dopamine and norepinephrine turnover in various regions of the rat brain after chronic manganese chloride administration. Toxicology. 1982;24:175–182. - PubMed
-
- Borowsky RD, Hoffman BJ. Neurotransmitter transporters: molecular biology, function, and regulation. Int Rev Neurobiol. 1995;38:139–199. - PubMed
-
- Burdo JR, Martin J, Menzies SL, Dolan KG, Romano MA, Fletcher RJ, Garrick MD, Garrick LM, Connor JR. Cellular distribution of iron in the brain of the Belgrade rat. Neuroscience. 1999;93:1189–1196. - PubMed
-
- Connor J, Menzies S, Burdo J, Boyer P. Iron and iron management proteins in neurobiology. Pediatr Neurol. 2001;25:118–129. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

