The influence of a PHI-5-loaded silicone membrane, on cutaneous wound healing in vivo
- PMID: 17387598
- PMCID: PMC1915588
- DOI: 10.1007/s10856-006-0112-z
The influence of a PHI-5-loaded silicone membrane, on cutaneous wound healing in vivo
Abstract
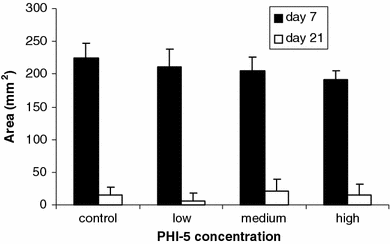
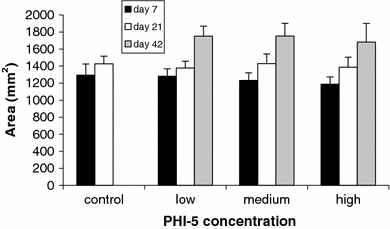
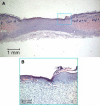
This study investigated whether a novel ionogenic substance, containing amongst others zinc and rubidium (PHI-5; Dermagenics Inc, Memphis, TN, USA), could improve the healing of full-thickness skin wounds. Uniform wounds were created on the right flank of guinea pigs. Micro-grooved silicone rubber membranes, containing 0 (controls), 1.25, 5.00, or 10.00 microg PHI-5, were sutured onto this wound. Standardized digital wound photographs were made after 1, 3, and 6 weeks. Also, wound biopsies were taken after 3 and 6 weeks for histological and histomorphometrical evaluation. For all study groups, 6 animals were used. Analysis of the 1-week digital photographs showed that the surface area of the wounds decreased significantly, with an increasing PHI-5 concentration. No other differences were found in the wound photographs. Also, no differences were measured in histomorphometry at 3 and 6 weeks. Concluding, in our study model a single application of PHI-5 did have a significant positive influence on initial wound healing.
Figures





Similar articles
-
A comparative study of three occlusive dressings in the treatment of full-thickness wounds in pigs.J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997 Jan;36(1):53-8. doi: 10.1016/s0190-9622(97)70325-6. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1997. PMID: 8996261
-
Functionalized silk biomaterials for wound healing.Adv Healthc Mater. 2013 Jan;2(1):206-17. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201200192. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Adv Healthc Mater. 2013. PMID: 23184644 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The combined effect of recombinant human epidermal growth factor and erythropoietin on full-thickness wound healing in diabetic rat model.Int Wound J. 2014 Aug;11(4):373-8. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-481X.2012.01100.x. Epub 2012 Oct 19. Int Wound J. 2014. PMID: 23078553 Free PMC article.
-
Overview of Silk Fibroin Use in Wound Dressings.Trends Biotechnol. 2018 Sep;36(9):907-922. doi: 10.1016/j.tibtech.2018.04.004. Epub 2018 May 12. Trends Biotechnol. 2018. PMID: 29764691 Review.
-
Advances in wound care and healing technology.Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000 Sep-Oct;1(5):269-75. doi: 10.2165/00128071-200001050-00002. Am J Clin Dermatol. 2000. PMID: 11702318 Review.
Cited by
-
Synthesis and evaluation of novel absorptive and antibacterial polyurethane membranes as wound dressing.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012 Sep;23(9):2187-202. doi: 10.1007/s10856-012-4683-6. Epub 2012 May 26. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2012. PMID: 22639152
-
Epidermal and fibroblast growth factors incorporated polyvinyl alcohol electrospun nanofibers as biological dressing scaffold.Sci Rep. 2021 Mar 11;11(1):5634. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-85149-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33707606 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Patent Dermagenics Europe B.V. Dressing material and dressings for the treatment of wounds. Madrid Registration No. 780930. 2002 Mar 12
-
- R. B. KARIM, A. K. J. AHMED, B. L. R. BRITO et al. Balancing MMPs in chronic wounds: a pilot study with Dermax. Abstract Dutch Association for Plastic Surgery, Aalst, Belgium, 2002 Nov 23
-
- A. B. WYSOCKI, L. STAIANO-COICO and F. GRINNELL, J. Invest. Dermatol.101(1) (1993) 64 - PubMed
-
- D. R. YAGER, L. Y. ZHANG, H. X. LIANG, R. F. DIEGELMANN and I. K. COHEN, J. Invest. Dermatol.107(5) (1996) 743 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

