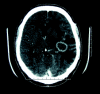
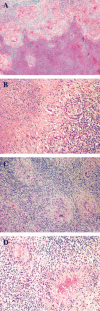
November 2006: a 39-year-old man with new onset seizures
- PMID: 17388957
- PMCID: PMC8095640
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00068_2.x
November 2006: a 39-year-old man with new onset seizures
References
-
- Al‐Deeb SM, Yaqub BA, Sharif HS, Motaery KR (1992) Neurotuberculosis: a review. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 94(Suppl.):S30–S33. - PubMed
-
- Al Soub H, Al Alousi FS, Al‐Khal AL (2001) Tuberculoma of the cavernous sinus. Scand J Infect Dis 33:868–870. - PubMed
-
- Artico M, De Caro GM, Carloia S, Salvati M, D’Ambrosio M, Delfini R (1999) Advances in diagnosis, treatment and prognosis of intracerebral tuberculomas in the last 50 years. Report of 21 cases. Neurochirurgie 45:129–133. - PubMed
-
- Dastur HM (1983) Diagnosis and neurosurgical treatment of tuberculous disease of the CNS. Neurosurg Rev 6:111–117. - PubMed
-
- DeAngelis LM (1981) Intracranial tuberculoma: case report and review of the literature. Neurology 31:1133–1136. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical