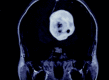
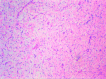
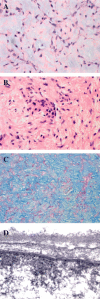
December 2006: 31-year-old woman with hemiparesis
- PMID: 17388958
- PMCID: PMC8095548
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1750-3639.2007.00068_3.x
December 2006: 31-year-old woman with hemiparesis
References
-
- Antonescu C, Ladanyi M (2002) Myxoid liposarcomas. In: Tumours of Soft Tissue and Bone. Christopher DM, Fletcher K, Unni K, Mertens F (eds), pp. 40–43. IARC press: Lyon.
-
- Begin LR (1990) Myxoid meningioma. Ultrastruct Pathol 14:367–374. - PubMed
-
- Dahmen HG (1979) Studies on mucinous substances in myxomatous meningiomas. Acta Neuropathol 48:235–237. - PubMed
-
- Graham JF, Loo SYT, Matoba A (1999) Primary brain myxoma, an unusual tumor of meningeal origin: case report. Neurosurgery 45:166–169. - PubMed
-
- Harrison JD, Rose PE (1985) Myxoid meningioma: histochemistry and electron microscopy. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 68:80–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical