Alteration of epithelial structure and function associated with PtdIns(4,5)P2 degradation by a bacterial phosphatase
- PMID: 17389247
- PMCID: PMC2151621
- DOI: 10.1085/jgp.200609656
Alteration of epithelial structure and function associated with PtdIns(4,5)P2 degradation by a bacterial phosphatase
Abstract
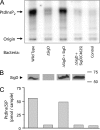
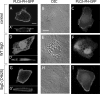
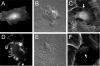
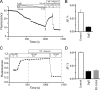
Elucidation of the role of PtdIns(4,5)P(2) in epithelial function has been hampered by the inability to selectively manipulate the cellular content of this phosphoinositide. Here we report that SigD, a phosphatase derived from Salmonella, can effectively hydrolyze PtdIns(4,5)P(2), generating PtdIns(5)P. When expressed by microinjecting cDNA into epithelial cells forming confluent monolayers, wild-type SigD induced striking morphological and functional changes that were not mimicked by a phosphatase-deficient SigD mutant (C462S). Depletion of PtdIns(4,5)P(2) in intact SigD-injected cells was verified by detachment from the membrane of the pleckstrin homology domain of phospholipase Cdelta, used as a probe for the phosphoinositide by conjugation to green fluorescent protein. Single-cell measurements of cytosolic pH indicated that the Na(+)/H(+) exchange activity of epithelia was markedly inhibited by depletion of PtdIns(4,5)P(2). Similarly, anion permeability, measured using two different halide-sensitive probes, was depressed in cells expressing SigD. Depletion of PtdIns(4,5)P(2) was associated with marked alterations in the actin cytoskeleton and its association with the plasma membrane. The junctional complexes surrounding the injected cells gradually opened and the PtdIns(4,5)P(2)-depleted cells eventually detached from the monolayer, which underwent rapid restitution. Similar observations were made in intestinal and renal epithelial cultures. In addition to its effects on phosphoinositides, SigD has been shown to convert inositol 1,3,4,5,6-pentakisphosphate (IP(5)) into inositol 1,4,5,6-tetrakisphosphate (IP(4)), and the latter has been postulated to mediate the diarrhea caused by Salmonella. However, the effects of SigD on epithelial cells were not mimicked by microinjection of IP(4). In contrast, the cytoskeletal and ion transport effects were replicated by hydrolyzing PtdIns(4,5)P(2) with a membrane-targeted 5-phosphatase or by occluding the inositide using high-avidity tandem PH domain constructs. We therefore suggest that opening of the tight junctions and inhibition of Na(+)/H(+) exchange caused by PtdIns(4,5)P(2) hydrolysis combine to account, at least in part, for the fluid loss observed during Salmonella-induced diarrhea.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Elimination of host cell PtdIns(4,5)P(2) by bacterial SigD promotes membrane fission during invasion by Salmonella.Nat Cell Biol. 2002 Oct;4(10):766-73. doi: 10.1038/ncb854. Nat Cell Biol. 2002. PMID: 12360287
-
Annexin 2 is a phosphatidylinositol (4,5)-bisphosphate binding protein recruited to actin assembly sites at cellular membranes.J Cell Sci. 2004 Jul 15;117(Pt 16):3473-80. doi: 10.1242/jcs.01208. Epub 2004 Jun 29. J Cell Sci. 2004. PMID: 15226372
-
Modulation of chloride secretory responses and barrier function of intestinal epithelial cells by the Salmonella effector protein SigD.Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004 Oct;287(4):C939-48. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.00413.2003. Epub 2004 Jun 2. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2004. PMID: 15175224
-
Phosphoinositides: Lipids with informative heads and mastermind functions in cell division.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015 Jun;1851(6):832-43. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2014.10.013. Epub 2014 Nov 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015. PMID: 25449648 Review.
-
How PI3K-derived lipids control cell division.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015 Sep 30;3:61. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2015.00061. eCollection 2015. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26484344 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
PI(4,5)P2: signaling the plasma membrane.Biochem J. 2022 Nov 11;479(21):2311-2325. doi: 10.1042/BCJ20220445. Biochem J. 2022. PMID: 36367756 Free PMC article.
-
Bacterial toxin effector-membrane targeting: outside in, then back again.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012 May 31;2:75. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2012.00075. eCollection 2012. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22919666 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production of phosphatidylinositol 5-phosphate via PIKfyve and MTMR3 regulates cell migration.EMBO Rep. 2013 Jan;14(1):57-64. doi: 10.1038/embor.2012.183. Epub 2012 Nov 16. EMBO Rep. 2013. PMID: 23154468 Free PMC article.
-
Depletion of PtdIns(4,5)P₂ underlies retinal degeneration in Drosophila trp mutants.J Cell Sci. 2013 Mar 1;126(Pt 5):1247-59. doi: 10.1242/jcs.120592. Epub 2013 Feb 1. J Cell Sci. 2013. PMID: 23378018 Free PMC article.
-
PtdIns5P activates the host cell PI3-kinase/Akt pathway during Shigella flexneri infection.EMBO J. 2006 Mar 8;25(5):1024-34. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601001. Epub 2006 Feb 16. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16482216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baumgartner, M., H. Patel, and D.L. Barber. 2004. Na+/H+ exchanger NHE1 as plasma membrane scaffold in the assembly of signaling complexes. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 287:C844–C850. - PubMed
-
- Bertelsen, L.S., G. Paesold, S.L. Marcus, B.B. Finlay, L. Eckmann, and K.E. Barrett. 2004. Modulation of chloride secretory responses and barrier function of intestinal epithelial cells by the Salmonella effector protein SigD. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 287:C939–C948. - PubMed
-
- Bretscher, A., K. Edwards, and R.G. Fehon. 2002. ERM proteins and merlin: integrators at the cell cortex. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 3:586–599. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

