Human islet isolation and allotransplantation in 22 consecutive cases
- PMID: 1738936
- PMCID: PMC2967200
- DOI: 10.1097/00007890-199202010-00027
Human islet isolation and allotransplantation in 22 consecutive cases
Abstract
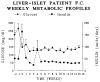
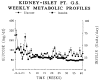
This report provides our initial experience in islet isolation and intrahepatic allotransplantation in 21 patients. In group 1, 10 patients underwent combined liver-islet allotransplantation following upper-abdominal exenteration for cancer. In group 2, 4 patients received a combined liver-islet allograft for cirrhosis and diabetes. One patients had plasma C-peptide greater than 3 pM and was therefore excluded from analysis. In group 3, 7 patients received 8 combined cadaveric kidney-islet grafts (one retransplant) for end-stage renal disease secondary to type 1 diabetes mellitus. The islets were separated by a modification of the automated method for human islet isolation and the preparation were infused into the portal vein. Immunosuppression was with FK506 (group 1) plus steroids (groups 2 and 3). Six patients in group 1 did not require insulin treatment for 5 to greater than 16 months. In groups 2 and 3 none of the patients became insulin-independent, although decreased insulin requirement and stabilization of diabetes were observed. Our results indicate that rejection is still a major factor limiting the clinical application of islet transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus, although other factors such as steroid treatment may contribute to deteriorate islet engraftment and/or function.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Outcome of human islet isolation and allotransplantation in 20 consecutive cases.Diabetes Nutr Metab. 1992;5 Suppl 1:193-198. Diabetes Nutr Metab. 1992. PMID: 21572935 Free PMC article.
-
Achievement of insulin independence in three consecutive type-1 diabetic patients via pancreatic islet transplantation using islets isolated at a remote islet isolation center.Transplantation. 2002 Dec 27;74(12):1761-6. doi: 10.1097/00007890-200212270-00020. Transplantation. 2002. PMID: 12499894
-
Improved human pancreatic islet isolation for a prospective cohort study of islet transplantation vs best medical therapy in type 1 diabetes mellitus.Arch Surg. 2005 Aug;140(8):735-44. doi: 10.1001/archsurg.140.8.735. Arch Surg. 2005. PMID: 16103282
-
The Fate of Allogeneic Pancreatic Islets following Intraportal Transplantation: Challenges and Solutions.J Immunol Res. 2018 Sep 23;2018:2424586. doi: 10.1155/2018/2424586. eCollection 2018. J Immunol Res. 2018. PMID: 30345316 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical islet transplantation--registry report, accomplishments in the past and future research needs.Cell Transplant. 1993 Jul-Aug;2(4):269-82; discussion 283-305. doi: 10.1177/096368979300200403. Cell Transplant. 1993. PMID: 8162271 Review.
Cited by
-
The spectrum of action of new immunosuppressive drugs.Clin Exp Immunol. 1992 Aug;89(2):170-3. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1992.tb06927.x. Clin Exp Immunol. 1992. PMID: 1379130 Free PMC article. Review. No abstract available.
-
Recent advances in the management of diabetes mellitus.Indian J Pediatr. 1997 Jan-Feb;64(1):33-41. doi: 10.1007/BF02795774. Indian J Pediatr. 1997. PMID: 10771811 Review.
-
Engineering the lymph node environment promotes antigen-specific efficacy in type 1 diabetes and islet transplantation.Nat Commun. 2023 Feb 8;14(1):681. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-36225-5. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 36755035 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in Pancreatic Islet Transplantation Sites for the Treatment of Diabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Sep 13;12:732431. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.732431. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34589059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Dental Pulp Stem Cells Exhibit Osteogenic Differentiation Potential.Open Life Sci. 2020 May 6;15:229-236. doi: 10.1515/biol-2020-0023. eCollection 2020. Open Life Sci. 2020. PMID: 33987479 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Harris MI, Hanaman RF, editors. NIH publication No. 85–1468. Bethesda, MD: 1985. Diabetes in america.
-
- La Porte RE, Fishbirn HA, Drash AL, et al. The Pittsburgh insulin dependent diabetes mellitus (IDDM) registry: the incidence of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in Allegheny County, Pennsylvania (1965–1976) Diabetes. 1981;30:279. - PubMed
-
- Bennet PH. Epidemiology of diabetes mellitus. In: Rifkin H, Porte D Jr, editors. Diabetes mellitus: theory and practice. New York: Elsevier; 1990. p. 357.
-
- Krolewski AS, Warram JH, Rand LI, et al. Epidemiologic approach to the etiology of type 1 diabetes mellitus and its complications. N Engl J Med. 1987;317:1390. - PubMed
-
- Goetz FC, Elick B, Fryd D, Sutherland DER. Renal transplantation in diabetes. Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1986;15:807. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
