The role of pannexin 1 hemichannels in ATP release and cell-cell communication in mouse taste buds
- PMID: 17389364
- PMCID: PMC1851090
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611280104
The role of pannexin 1 hemichannels in ATP release and cell-cell communication in mouse taste buds
Abstract
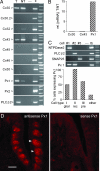
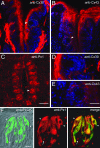
ATP has been shown to be a taste bud afferent transmitter, but the cells responsible for, and the mechanism of, its release have not been identified. Using CHO cells expressing high-affinity neurotransmitter receptors as biosensors, we show that gustatory stimuli cause receptor cells to secrete ATP through pannexin 1 hemichannels in mouse taste buds. ATP further stimulates other taste cells to release a second transmitter, serotonin. These results provide a mechanism to link intracellular Ca(2+) release during taste transduction to secretion of afferent transmitter, ATP, from receptor cells. They also indicate a route for cell-cell communication and signal processing within the taste bud.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
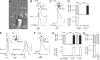

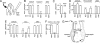
Similar articles
-
Cell-to-cell communication in intact taste buds through ATP signalling from pannexin 1 gap junction hemichannels.J Physiol. 2009 Dec 15;587(Pt 24):5899-906. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.180083. J Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19884319 Free PMC article.
-
Calcitonin Gene-Related Peptide Reduces Taste-Evoked ATP Secretion from Mouse Taste Buds.J Neurosci. 2015 Sep 16;35(37):12714-24. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0100-15.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 26377461 Free PMC article.
-
Afferent neurotransmission mediated by hemichannels in mammalian taste cells.EMBO J. 2007 Feb 7;26(3):657-67. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601526. Epub 2007 Jan 18. EMBO J. 2007. PMID: 17235286 Free PMC article.
-
Cell communication in taste buds.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006 Jul;63(13):1494-500. doi: 10.1007/s00018-006-6112-9. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2006. PMID: 16732426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Signal transduction and information processing in mammalian taste buds.Pflugers Arch. 2007 Aug;454(5):759-76. doi: 10.1007/s00424-007-0247-x. Epub 2007 Apr 28. Pflugers Arch. 2007. PMID: 17468883 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Honing in on the ATP Release Channel in Taste Cells.Chem Senses. 2015 Sep;40(7):449-51. doi: 10.1093/chemse/bjv035. Epub 2015 Jun 30. Chem Senses. 2015. PMID: 26126730 Free PMC article.
-
Glucagon-like peptide-1 is specifically involved in sweet taste transmission.FASEB J. 2015 Jun;29(6):2268-80. doi: 10.1096/fj.14-265355. Epub 2015 Feb 12. FASEB J. 2015. PMID: 25678625 Free PMC article.
-
Chemosensory epithelial cells in the urethra: sentinels of the urinary tract.Histochem Cell Biol. 2016 Dec;146(6):673-683. doi: 10.1007/s00418-016-1504-x. Epub 2016 Sep 29. Histochem Cell Biol. 2016. PMID: 27680547 Review.
-
Mammalian Taste Bud Cells Utilize Extragemmal 5-Hydroxy-L-Tryptophan to Biosynthesize the Neurotransmitter Serotonin.Front Cell Neurosci. 2018 Nov 26;12:461. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2018.00461. eCollection 2018. Front Cell Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30534058 Free PMC article.
-
Sodium/calcium exchangers selectively regulate calcium signaling in mouse taste receptor cells.J Neurophysiol. 2010 Jul;104(1):529-38. doi: 10.1152/jn.00118.2010. Epub 2010 May 12. J Neurophysiol. 2010. PMID: 20463203 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

