The role of pannexin 1 hemichannels in ATP release and cell-cell communication in mouse taste buds
- PMID: 17389364
- PMCID: PMC1851090
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0611280104
The role of pannexin 1 hemichannels in ATP release and cell-cell communication in mouse taste buds
Abstract
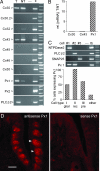
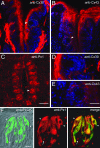
ATP has been shown to be a taste bud afferent transmitter, but the cells responsible for, and the mechanism of, its release have not been identified. Using CHO cells expressing high-affinity neurotransmitter receptors as biosensors, we show that gustatory stimuli cause receptor cells to secrete ATP through pannexin 1 hemichannels in mouse taste buds. ATP further stimulates other taste cells to release a second transmitter, serotonin. These results provide a mechanism to link intracellular Ca(2+) release during taste transduction to secretion of afferent transmitter, ATP, from receptor cells. They also indicate a route for cell-cell communication and signal processing within the taste bud.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
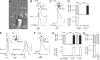

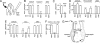
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

