Molecular and electrophysiological characterization of a mechanosensitive channel expressed in the chloroplasts of Chlamydomonas
- PMID: 17389370
- PMCID: PMC1851586
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0609996104
Molecular and electrophysiological characterization of a mechanosensitive channel expressed in the chloroplasts of Chlamydomonas
Abstract
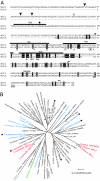
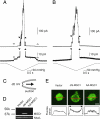
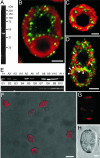
MscS is a mechanosensitive channel that is ubiquitous among bacteria. Recent progress in the genome projects has revealed that homologs of MscS are also present in eukaryotes, but whether they operate as ion channels is unknown. In this study we cloned MSC1, a homolog of MscS in Chlamydomonas, and examined its function when expressed in Escherichia coli. Full-length MSC1 was not functional when expressed in E. coli cells. However, removal of the N-terminal signal sequence (DeltaN-MSC1) reversed this effect. DeltaN-MSC1 was found to open in response to membrane stretch and displayed a preference for anions over cations as permeable ions. DeltaN-MSC1 exhibited marked hysteretic behavior in response to ascending and descending stimuli. That is, channel gating occurred in response to significant stimuli but remained open until the stimulus was almost completely removed. Indirect immunofluorescence revealed that MSC1 is present as punctate spots in the cytoplasm and chloroplasts. Moreover, knockdown of MSC1 expression resulted in the abnormal localization of chlorophyll. These findings show that MSC1 is an intracellular mechanosensitive channel and is responsible for the organization of chloroplast in Chlamydomonas.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

