Thymulin gene therapy prevents the reduction in circulating gonadotropins induced by thymulin deficiency in mice
- PMID: 17389714
- PMCID: PMC2656608
- DOI: 10.1152/ajpendo.00085.2007
Thymulin gene therapy prevents the reduction in circulating gonadotropins induced by thymulin deficiency in mice
Abstract
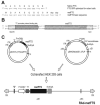
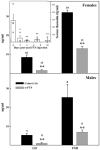
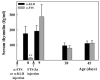
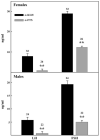
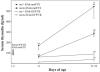
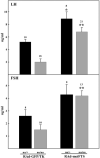
Integrity of the thymus during perinatal life is necessary for a proper maturation of the pituitary-gonadal axis in mice and other mammalian species. Thus congenitally athymic (nude) female mice show significantly reduced levels of circulating gonadotropins, a fact that seems to be causally related to a number of reproductive derangements described in these mutants. Interestingly, a number of in vitro studies suggest that the thymic peptide thymulin may be involved in thymus-pituitary communication. To determine the consequences of low serum thymulin in otherwise normal animals, we induced short (8 days)- and long (33 days)-term thymulin deficiency in C57BL/6 mice by neonatally injecting (intraperitoneally) an anti-thymulin serum and assessed their circulating gonadotropin levels at puberty and thereafter. Control mice received an irrelevant antiserum. Gonadotropins were measured by radioimmunoassay and thymulin by bioassay. Both long- and short-term serum thymulin immunoneutralization resulted in a significant reduction in the serum levels of gonadotropins at 33 and 45 days of age. Subsequently, we injected (intramuscularly) an adenoviral vector harboring a synthetic DNA sequence (5'-ATGCAAGCCAAATCTCAAGGTGGATCCAACTAGTAG-3') encoding a biologically active analog of thymulin, methionine-FTS, in newborn nude mice (which are thymulin deficient) and measured circulating gonadotropin levels when the animals reached 52 days of age. It was observed that neonatal thymulin gene therapy in the athymic mice restored their serum thymulin levels and prevented the reduction in circulating gonadotropin levels that typically emerges in these mutants after puberty. Our results indicate that thymulin plays a relevant physiological role in the thymus-pituitary-gonadal axis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Neonatal thymulin gene therapy prevents ovarian dysgenesis and attenuates reproductive derangements in nude female mice.Endocrinology. 2012 Aug;153(8):3922-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1183. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22700775 Free PMC article.
-
Morphological restoration of gonadotrope population by thymulin gene therapy in nude mice.Histol Histopathol. 2009 Jun;24(6):729-35. doi: 10.14670/HH-24.729. Histol Histopathol. 2009. PMID: 19337971 Free PMC article.
-
Neonatal thymulin gene therapy in nude mice: Effects on the morphology of the pituitary corticotrope population.Histol Histopathol. 2011 Apr;26(4):471-9. doi: 10.14670/HH-26.471. Histol Histopathol. 2011. PMID: 21360440
-
Potential of gene therapy for restoration of endocrine thymic function in thymus-deficient animal models.Curr Gene Ther. 2008 Feb;8(1):49-53. doi: 10.2174/156652308783688518. Curr Gene Ther. 2008. PMID: 18336249 Review.
-
The thymus-neuroendocrine axis: physiology, molecular biology, and therapeutic potential of the thymic peptide thymulin.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009 Feb;1153:98-106. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2008.03964.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009. PMID: 19236333 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Neonatal thymulin gene therapy prevents ovarian dysgenesis and attenuates reproductive derangements in nude female mice.Endocrinology. 2012 Aug;153(8):3922-8. doi: 10.1210/en.2012-1183. Epub 2012 Jun 14. Endocrinology. 2012. PMID: 22700775 Free PMC article.
-
Thymulin-based gene therapy and pituitary function in animal models of aging.Neuroimmunomodulation. 2011;18(5):350-6. doi: 10.1159/000329495. Epub 2011 Sep 22. Neuroimmunomodulation. 2011. PMID: 21952687 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of the immune system on ovarian function and features of ovarian germline stem cells.Springerplus. 2016 Jul 7;5(1):990. doi: 10.1186/s40064-016-2390-3. eCollection 2016. Springerplus. 2016. PMID: 27398269 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA nanoparticle-mediated thymulin gene therapy prevents airway remodeling in experimental allergic asthma.J Control Release. 2014 Apr 28;180:125-33. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.02.010. Epub 2014 Feb 17. J Control Release. 2014. PMID: 24556417 Free PMC article.
-
Female germline stem cells: aging and anti-aging.J Ovarian Res. 2022 Jul 4;15(1):79. doi: 10.1186/s13048-022-01011-2. J Ovarian Res. 2022. PMID: 35787298 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bach JF. Thymulin (FTS-Zn) Clin Immunol Allergy. 1983;3:133–156.
-
- Besedovsky HO, Sorkin E. Thymus involvement in female sexual maturation. Nature. 1974;249:356–358. - PubMed
-
- Brown OA, Sosa YE, Bolognani F, Goya RG. Thymulin stimulates prolactin and thyrotropin release in an age-related manner. Mech Ageing Dev. 1998;104:249–262. - PubMed
-
- Brown OA, Sosa YE, Dardenne M, Pléau JM, Goya RG. Growth hormone-releasing activity of thymulin: effects of age. Neuroendocrinology. 1999;69:20–27. - PubMed
-
- Brown OA, Sosa YE, Dardenne M, Pléau JM, Goya RG. Studies on the gonadotropin-releasing activity of thymulin: changes with age. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2000;55:B170–B176. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

