Prediction of phenotype and gene expression for combinations of mutations
- PMID: 17389876
- PMCID: PMC1847951
- DOI: 10.1038/msb4100137
Prediction of phenotype and gene expression for combinations of mutations
Abstract
Molecular interactions provide paths for information flows. Genetic interactions reveal active information flows and reflect their functional consequences. We integrated these complementary data types to model the transcription network controlling cell differentiation in yeast. Genetic interactions were inferred from linear decomposition of gene expression data and were used to direct the construction of a molecular interaction network mediating these genetic effects. This network included both known and novel regulatory influences, and predicted genetic interactions. For corresponding combinations of mutations, the network model predicted quantitative gene expression profiles and precise phenotypic effects. Multiple predictions were tested and verified.
Figures
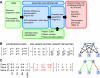
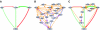
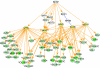
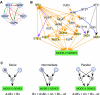
References
-
- Ashburner M, Ball CA, Blake JA, Botstein D, Butler H, Cherry JM, Davis AP, Dolinski K, Dwight SS, Eppig JT, Harris MA, Hill DP, Issel-Tarver L, Kasarskis A, Lewis S, Matese JC, Richardson JE, Ringwald M, Rubin GM, Sherlock G (2000) Gene ontology: tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat Genet 25: 25–29 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barton NH, Keightley PD (2002) Understanding quantitative genetic variation. Nat Rev Genet 3: 11–21 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

