Endogenous glucocorticoids protect against TNF-alpha-induced increases in anxiety-like behavior in virally infected mice
- PMID: 17389906
- PMCID: PMC3392959
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.mp.4001921
Endogenous glucocorticoids protect against TNF-alpha-induced increases in anxiety-like behavior in virally infected mice
Abstract
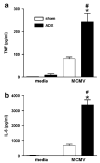
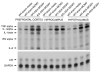
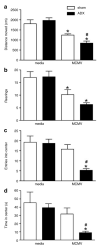
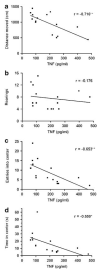
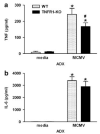
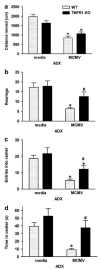
Endogenous glucocorticoids restrain proinflammatory cytokine responses to immune challenges such as viral infection. In addition, proinflammatory cytokines induce behavioral alterations including changes in locomotor/exploratory activity. Accordingly, we examined proinflammatory cytokines and open-field behavior in virally infected mice rendered glucocorticoid deficient by adrenalectomy (ADX). Mice were infected with murine cytomegalovirus (MCMV), and open-field behavior (36 h post-infection) and plasma concentrations of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and interleukin (IL)-6 (42 h post-infection) were assessed. Compared to sham-ADX-MCMV-infected animals, ADX-MCMV-infected mice exhibited significant reductions in total distance moved, number of center entries, and time spent in center. These behavioral alterations were accompanied by significantly higher plasma concentrations of TNF-alpha and IL-6, both of which were correlated with degree of behavioral change. To examine the role of TNF-alpha in these behavioral alterations, open-field behavior was compared in wild-type (WT) and TNF-R1-knockout (KO), ADX-MCMV-infected mice. TNF-R1-KO mice exhibited significantly attenuated decreases in number of rearings, number of center entries and time spent in center, but not distance moved, which correlated with plasma IL-6. Given the potential role of brain cytokines in these findings, mRNA expression of TNF-alpha, IL-1 and IL-6 was assessed in various brain regions. Although MCMV induced increases in proinflammatory cytokine mRNA throughout the brain (especially in ADX animals), no remarkable differences were found between WT and TNF-R1-KO mice. These results demonstrate that endogenous glucocorticoids restrain proinflammatory cytokine responses to viral infection and their impact on locomotor/exploratory activity. Moreover, TNF-alpha appears to mediate cytokine-induced changes in open-field behaviors, especially those believed to reflect anxiety.
Figures
References
-
- Turnbull AV, Rivier CL. Regulation of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis by cytokines: actions and mechanisms of action. Physiol Rev. 1999;79:1–71. - PubMed
-
- Silverman MN, Miller AH, Biron CA, Pearce BD. Characterization of an interleukin-6- and adrenocorticotropin-dependent, immune-to-adrenal pathway during viral infection. Endocrinology. 2004;145:3580–3589. - PubMed
-
- Glezer I, Rivest S. Glucocorticoids: protectors of the brain during innate immune responses. Neuroscientist. 2004;10:538–552. - PubMed
-
- Miller AH, Pearce BD, Ruzek MC, Biron CA. Interactions between the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis and immune system during viral infection: pathways for environmental effects on disease expression. In: McEwen BS, editor. Handbook of Physiology. Oxford University Press; New York: 2001. pp. 425–450.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

