Structural stability and endonuclease activity of a PI-SceI GFP-fusion protein
- PMID: 17389927
- PMCID: PMC1802021
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.3.205
Structural stability and endonuclease activity of a PI-SceI GFP-fusion protein
Abstract
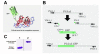
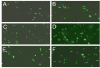
Homing endonucleases are site-specific and rare cutting endonucleases often encoded by intron or intein containing genes. They lead to the rapid spread of the genetic element that hosts them by a process termed 'homing'; and ultimately the allele containing the element will be fixed in the population. PI-SceI, an endonuclease encoded as a protein insert or intein within the yeast V-ATPase catalytic subunit encoding gene (vma1), is among the best characterized homing endonucleases. The structures of the Sce VMA1 intein and of the intein bound to its target site are known. Extensive biochemical studies performed on the PI-SceI enzyme provide information useful to recognize critical amino acids involved in self-splicing and endonuclease functions of the protein. Here we describe an insertion of the Green Fluorescence Protein (GFP) into a loop which is located between the endonuclease and splicing domains of the Sce VMA1 intein. The GFP is functional and the additional GFP domain does not prevent intein excision and endonuclease activity. However, the endonuclease activity of the newly engineered protein was different from the wild-type protein in that it required the presence of Mn(2+) and not Mg(2+) metal cations for activity.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists.
Figures
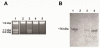
Similar articles
-
Chimeras of the homing endonuclease PI-SceI and the homologous Candida tropicalis intein: a study to explore the possibility of exchanging DNA-binding modules to obtain highly specific endonucleases with altered specificity.Chembiochem. 2004 Feb 6;5(2):206-13. doi: 10.1002/cbic.200300718. Chembiochem. 2004. PMID: 14760742
-
Homology modeling and mutational analysis of Ho endonuclease of yeast.Genetics. 2004 Feb;166(2):721-8. doi: 10.1534/genetics.166.2.721. Genetics. 2004. PMID: 15020462 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of I-SceI homing endonucleases with increased DNA recognition site specificity.J Mol Biol. 2011 Jan 7;405(1):185-200. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2010.10.029. Epub 2010 Oct 26. J Mol Biol. 2011. PMID: 21029741 Free PMC article.
-
Reflections on protein splicing: structures, functions and mechanisms.Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2009;85(9):409-21. doi: 10.2183/pjab.85.409. Proc Jpn Acad Ser B Phys Biol Sci. 2009. PMID: 19907126 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel site-specific DNA endonucleases.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998 Feb;8(1):19-25. doi: 10.1016/s0959-440x(98)80005-5. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 1998. PMID: 9519292 Review.
Cited by
-
Fusion of GFP to the M.EcoKI DNA methyltransferase produces a new probe of Type I DNA restriction and modification enzymes.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010 Jul 23;398(2):254-9. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2010.06.069. Epub 2010 Jun 19. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2010. PMID: 20599730 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

