Characterization of transcriptional regulation of neurogranin by nitric oxide and the role of neurogranin in SNP-induced cell death: implication of neurogranin in an increased neuronal susceptibility to oxidative stress
- PMID: 17389928
- PMCID: PMC1820875
- DOI: 10.7150/ijbs.3.212
Characterization of transcriptional regulation of neurogranin by nitric oxide and the role of neurogranin in SNP-induced cell death: implication of neurogranin in an increased neuronal susceptibility to oxidative stress
Abstract
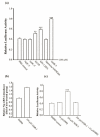
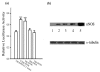
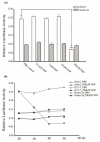
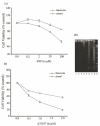
Neurogranin (Ng), a calmodulin (CaM)-binding protein kinase C (PKC) substrate, regulates the availability of Ca(2+)/CaM complex and modulates the homeostasis of intracellular calcium in neurons. Previous work showed Ng oxidation by NO donor induces increase in [Ca(2+)](i). The current study demonstrated that the gene transcription of Ng could be up-regulated by various nitric oxide (NO) donors via a NO-soluble guanylyl cyclase (sGC)-mediated pathway. Furthermore, ectopic expression of neuronal nitric oxide synthase (nNOS) in human embryonic kidney 293 cells (HEK 293) exhibited a nNOS-concentration-dependent biphasic regulatory effect on Ng gene transcription. One of the NO donors, sodium nitroprusside (SNP), however, induced cell death of neuroblastoma Neuro-2a cells. The potency of SNP-induced cell death was shown to be higher in Neuro-2a cells expressing recombinant Ng, as compared with Neuro-2a control cells without Ng expression in cell viability and apoptosis assays. Single-cell fluorescence imaging and site-directed mutagenesis studies suggest that Ng promotes SNP-induced cell death through an amplification of calcium-mediated signaling, which requires the interaction between CaM and IQ motif of Ng. Increased neuronal susceptibility rendered by Ng in response to pathophysiological NO production is suggested to be involved in the selective vulnerability of neurons to oxidative insults in the CNS.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interests: The authors have declared that no conflict of interest exists
Figures

Similar articles
-
Small proteins that modulate calmodulin-dependent signal transduction: effects of PEP-19, neuromodulin, and neurogranin on enzyme activation and cellular homeostasis.Mol Neurobiol. 2000 Aug-Dec;22(1-3):99-113. doi: 10.1385/MN:22:1-3:099. Mol Neurobiol. 2000. PMID: 11414283 Review.
-
CaM kinase II activation and phospholamban phosphorylation by SNP in murine gastric antrum smooth muscles.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007 Apr;292(4):G1045-54. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00203.2006. Epub 2006 Dec 21. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2007. PMID: 17185633
-
Neurogranin expression in stably transfected N2A cell line affects cytosolic calcium level by nitric oxide stimulation.Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004 Oct 22;129(1-2):171-8. doi: 10.1016/j.molbrainres.2004.06.039. Brain Res Mol Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 15469893
-
Proteomics analysis of the expression of neurogranin in murine neuroblastoma (Neuro-2a) cells reveals its involvement for cell differentiation.Int J Biol Sci. 2007 Apr 19;3(5):263-73. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.3.263. Int J Biol Sci. 2007. PMID: 17505539 Free PMC article.
-
[Neurogranin: a brain-specific protein].Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2003 Apr;34(2):111-5. Sheng Li Ke Xue Jin Zhan. 2003. PMID: 12889141 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Toxicity and antibacterial assessment of chitosan-coated silver nanoparticles on human pathogens and macrophage cells.Int J Nanomedicine. 2012;7:1805-18. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S28077. Epub 2012 Apr 3. Int J Nanomedicine. 2012. PMID: 22619529 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of the brain-specific neurogranin gene in murine T-cell lymphomas by proviral insertional mutagenesis.Gene. 2009 Aug 1;442(1-2):55-62. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2009.04.003. Epub 2009 Apr 17. Gene. 2009. PMID: 19376211 Free PMC article.
-
The calmodulin regulator protein, PEP-19, sensitizes ATP-induced Ca2+ release.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 18;288(3):2040-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.411314. Epub 2012 Nov 30. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23204517 Free PMC article.
-
Massively parallel signature sequencing and bioinformatics analysis identifies up-regulation of TGFBI and SOX4 in human glioblastoma.PLoS One. 2010 Apr 19;5(4):e10210. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010210. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20419098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gerendasy D.D, Sutcliffe J.G. RC3/neurogranin, a postsynaptic calpacitin for setting the response threshold to calcium influxes. Mol. Neurobiol. 1997;15:131–163. - PubMed
-
- Pak J.H, Huang F.L, Li J, Balschun D, Reymann K.G, Chiang C, Westphal H, Huang K.P. Involvement of neurogranin in the modulation of calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II, synaptic plasticity, and spatial learning: a study with knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2000;97:11232–11237. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Prichard L, Deloulme J.C, Storm D.R. Interactions between neurogranin and calmodulin in vivo. J. Biol. Chem. 1999;274:7689–7694. - PubMed
-
- Huang K.P, Huang F.L, Chen H.C. Characterization of a 7.5-kDa protein kinase C substrate (RC3 protein, neurogranin) from rat brain. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1993;305:570–580. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

