Bmi-1 is essential for the tumorigenicity of neuroblastoma cells
- PMID: 17392175
- PMCID: PMC1829469
- DOI: 10.2353/ajpath.2007.060754
Bmi-1 is essential for the tumorigenicity of neuroblastoma cells
Abstract
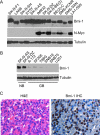
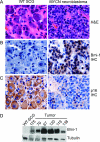
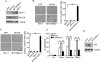
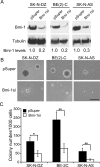
Activation of oncogenes underlies the pathogenesis of most human cancers. In neuroblastoma, amplification of the oncogene MYCN occurs in approximately 22% of cases and is associated with advanced stages of the disease and poor prognosis. Identification of other oncogenes that are consistently mutated or overexpressed in neuroblastoma is crucial for a molecular understanding of the pathogenic process. Here, we report that the oncogene Bmi-1 is highly expressed in human neuroblastoma cell lines and primary tumors. Neuroblastoma development in MYCN transgenic mice, an animal model for the human disease, was associated with a marked increase in the levels of Bmi-1 expression. Bmi-1 cooperated with MYCN in transformation of benign S-type neuroblastoma cells and avian neural crest cells by inhibiting the apoptotic activity of MYCN. Importantly, down-regulation of Bmi-1 impaired the ability of neuroblastoma cells to grow in soft agar and induce tumors in immunodeficient mice. Moreover, Bmi-1-knockdown neuroblastoma xenografts were characterized by a significant increase in the amount of Schwannian stroma, a histological feature associated with clinically favorable neuroblastomas. These findings suggest a crucial role for Bmi-1 in neuroblastoma pathogenesis and provide insights into the molecular basis of neuroblastoma heterogeneity.
Figures

References
-
- Brodeur GM. Neuroblastoma: biological insights into a clinical enigma. Nat Rev Cancer. 2003;3:203–216. - PubMed
-
- Schwab M. MYCN in neuronal tumours. Cancer Lett. 2004;204:179–187. - PubMed
-
- Maris JM, Matthay KK. Molecular biology of neuroblastoma. J Clin Oncol. 1999;17:2264–2279. - PubMed
-
- Haupt Y, Bath ML, Harris AW, Adams JM. Bmi-1 transgene induces lymphomas and collaborates with myc in tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 1993;8:3161–3164. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

