Hippocampal formation: shedding light on the influence of sex and stress on the brain
- PMID: 17395265
- PMCID: PMC2101766
- DOI: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2007.02.006
Hippocampal formation: shedding light on the influence of sex and stress on the brain
Abstract
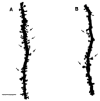
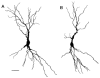
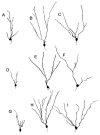
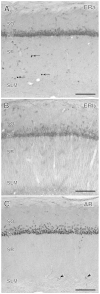
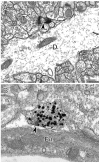
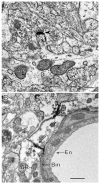
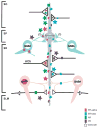
The hippocampus is a malleable brain region that responds to external agents such as hormones and stressors. Investigations that began in our laboratories with the Golgi technique and an appreciation of hippocampal neuroanatomy at the light and electron microscopic levels have led us down a path that has uncovered unexpected structural plasticity in the adult brain along with unanticipated cellular and molecular mechanisms of this plasticity and of hormone mediation of these effects. This chapter reviews the history of discoveries in our two laboratories involving the actions of estradiol and stress hormones on neuronal structure and function and then discusses the insight to hormone-brain interactions that this has engendered. These discoveries have led us to a new view of brain structural plasticity and the role and mechanism of steroid hormone action involving both genomic and non-genomic pathways. This new view is consistent with the predictions of Cajal in his book "The Structure of Ammon's horn", 1892.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Corticosteroids and hippocampal plasticity.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994 Nov 30;746:134-42; discussion 142-4, 178-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1994.tb39223.x. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1994. PMID: 7825871 Review.
-
Stress and the aging hippocampus.Front Neuroendocrinol. 1999 Jan;20(1):49-70. doi: 10.1006/frne.1998.0173. Front Neuroendocrinol. 1999. PMID: 9882536 Review.
-
Gonadal and adrenal steroids regulate neurochemical and structural plasticity of the hippocampus via cellular mechanisms involving NMDA receptors.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1996 Apr;16(2):103-16. doi: 10.1007/BF02088170. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 1996. PMID: 8743963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cell proliferation and cytogenesis in the mouse hippocampus.Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1991;122:1-74. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-76447-9. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1991. PMID: 1927657
-
Stress and hippocampal plasticity.Annu Rev Neurosci. 1999;22:105-22. doi: 10.1146/annurev.neuro.22.1.105. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10202533 Review.
Cited by
-
Chronic stress and brain plasticity: Mechanisms underlying adaptive and maladaptive changes and implications for stress-related CNS disorders.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015 Nov;58:79-91. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2015.06.018. Epub 2015 Jun 24. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2015. PMID: 26116544 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Effect of mineralocorticoid receptor blockade on hippocampal-dependent memory in adults with obesity.Obesity (Silver Spring). 2015 Jun;23(6):1136-42. doi: 10.1002/oby.21104. Epub 2015 May 9. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2015. PMID: 25959271 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Chronic corticosterone exposure alters postsynaptic protein levels of PSD-95, NR1, and synaptopodin in the mouse brain.Synapse. 2011 Aug;65(8):763-70. doi: 10.1002/syn.20900. Epub 2011 Apr 11. Synapse. 2011. PMID: 21190219 Free PMC article.
-
Sex Differences in the Subcellular Distribution of Corticotropin-Releasing Factor Receptor 1 in the Rat Hippocampus following Chronic Immobilization Stress.Neuroscience. 2018 Jul 15;383:98-113. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.05.007. Epub 2018 May 26. Neuroscience. 2018. PMID: 29753863 Free PMC article.
-
Social Determinants of Health, the developing brain, and risk and resilience for psychopathology.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025 Jul 16:10.1038/s41386-025-02169-1. doi: 10.1038/s41386-025-02169-1. Online ahead of print. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2025. PMID: 40670623 Review.
References
-
- Alves S, Weiland NG, Hayashi S, McEwen B. Immunocytochemical localization of nuclear estrogen receptors and progestin receptors within the dorsal raphe nucleus. J Comp Neurol. 1998;391:322–334. - PubMed
-
- Alves SE, McEwen BS, Hayashi S, Korach KS, Pfaff DW, Ogawa S. Estrogen-regulated progestin receptors are found in the midbrain raphe but not hippocampus of estrogen receptor alpha (ERα) gene-disrupted mice. J Comp Neurol. 2000;427:185–195. - PubMed
-
- Baker SW, Ehrhardt AA. Prenatal androgen, intelligence, and cognitive sex differences. In: Friedman RC, Richart RM, Vande Wiele RL, editors. Sex Differences in Behavior. New York: John Wiley & Sons, Inc; 1974. pp. 53–76.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

