Rat alpha6beta2delta GABAA receptors exhibit two distinct and separable agonist affinities
- PMID: 17395622
- PMCID: PMC2170852
- DOI: 10.1113/jphysiol.2007.132886
Rat alpha6beta2delta GABAA receptors exhibit two distinct and separable agonist affinities
Abstract
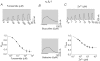
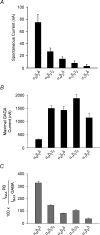
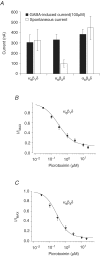
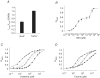
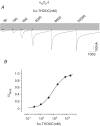
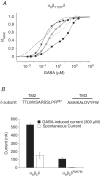
The onset of motor learning in rats coincides with exclusive expression of GABAA receptors containing alpha6 and delta subunits in the granule neurons of the cerebellum. This development temporally correlates with the presence of a spontaneously active chloride current through alpha6-containing GABAA receptors, known as tonic inhibition. Here we report that the coexpression of alpha6, beta2, and delta subunits produced receptor-channels which possessed two distinct and separable states of agonist affinity, one exhibiting micromolar and the other nanomolar affinities for GABA. The high-affinity state was associated with a significant level of spontaneous channel activity. Increasing the level of expression or the ratio of beta2 to alpha6 and delta subunits increased the prevalence of the high-affinity state. Comparative studies of alpha6beta2delta, alpha1beta2delta, alpha6beta2gamma2, alpha1beta2gamma2 and alpha4beta2delta receptors under equivalent levels of expression demonstrated that the significant level of spontaneous channel activity is uniquely attributable to alpha6beta2delta receptors. The pharmacology of spontaneous channel activity arising from alpha6beta2delta receptor expression corresponded to that of tonic inhibition. For example, GABAA receptor antagonists, including furosemide, blocked the spontaneous current. Further, the neuroactive steroid 5alpha-THDOC and classical glycine receptor agonists beta-alanine and taurine directly activated alpha6beta2delta receptors with high potency. Specific mutation within the GABA-dependent activation domain (betaY157F) impaired both low- and high-affinity components of GABA agonist activity in alpha6betaY157Fdelta receptors, but did not attenuate the spontaneous current. In comparison, a mutation located between the second and third transmembrane segments of the delta subunit (deltaR287M) significantly diminished the nanomolar component and the spontaneous activity. The possibility that the high affinity state of the alpha6beta2delta receptor modulates the granule neuron activity as well as potential mechanisms affecting its expression are discussed.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ketamine, but not phencyclidine, selectively modulates cerebellar GABA(A) receptors containing alpha6 and delta subunits.J Neurosci. 2008 May 14;28(20):5383-93. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5443-07.2008. J Neurosci. 2008. PMID: 18480294 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of GABA(A) receptor partial agonists in primary cultures of cerebellar granule neurons and cerebral cortical neurons reflect different receptor subunit compositions.Br J Pharmacol. 2001 Jun;133(4):539-49. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704121. Br J Pharmacol. 2001. PMID: 11399671 Free PMC article.
-
Dopamine directly modulates GABAA receptors.J Neurosci. 2015 Feb 25;35(8):3525-36. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4390-14.2015. J Neurosci. 2015. PMID: 25716851 Free PMC article.
-
Potency of GABA at human recombinant GABA(A) receptors expressed in Xenopus oocytes: a mini review.Amino Acids. 2013 Apr;44(4):1139-49. doi: 10.1007/s00726-012-1456-y. Epub 2013 Feb 6. Amino Acids. 2013. PMID: 23385381 Review.
-
Function and modulation of delta-containing GABA(A) receptors.Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009 Dec;34 Suppl 1:S67-73. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.08.010. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2009. PMID: 19766404 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Allosteric Regulation of Β-Ureidopropionase Depends on Fine-Tuned Stability of Active-Site Loops and Subunit Interfaces.Biomolecules. 2023 Dec 8;13(12):1763. doi: 10.3390/biom13121763. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 38136634 Free PMC article.
-
Agonist and antagonist properties of an insect GABA-gated chloride channel (RDL) are influenced by heterologous expression conditions.PLoS One. 2021 Jul 7;16(7):e0254251. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0254251. eCollection 2021. PLoS One. 2021. PMID: 34234379 Free PMC article.
-
Multiple roles for the first transmembrane domain of GABAA receptor subunits in neurosteroid modulation and spontaneous channel activity.Neurosci Lett. 2010 Apr 12;473(3):242-7. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2010.02.058. Epub 2010 Mar 1. Neurosci Lett. 2010. PMID: 20193738 Free PMC article.
-
The cerebellar Golgi cell and spatiotemporal organization of granular layer activity.Front Neural Circuits. 2013 May 17;7:93. doi: 10.3389/fncir.2013.00093. eCollection 2013. Front Neural Circuits. 2013. PMID: 23730271 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Discovery and rediscoveries of Golgi cells.J Physiol. 2010 Oct 1;588(Pt 19):3639-55. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2010.189605. J Physiol. 2010. PMID: 20581044 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amin J. A single hydrophobic residue confers barbiturate sensitivity to γ-aminobutyric acid type C receptor. Mol Pharmacol. 1999;55:411–423. - PubMed
-
- Amin J, Weiss DS. GABAA receptor needs two homologous domains of the β-subunit for activation by GABA but not by pentobarbital [see comment] Nature. 1993;366:565–569. - PubMed
-
- Amin J, Weiss DS. Insights into the activation mechanism of rho1 GABA receptors obtained by coexpression of wild type and activation-impaired subunits. Proc Biol Sci. 1996;263:273–282. - PubMed
-
- Baulac S, Huberfeld G, Gourfinkel-An I, Mitropoulou G, Beranger A, Prud'homme JF, Baulac M, Brice A, Bruzzone R, LeGuern E. First genetic evidence of GABAA receptor dysfunction in epilepsy: a mutation in the γ2-subunit gene. Nat Genet. 2001;28:46–48. - PubMed
-
- Baumann SW, Baur R, Sigel E. Subunit arrangement of γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptors. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:36275–36280. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

