Emergence of tempered preferential attachment from optimization
- PMID: 17395721
- PMCID: PMC1839059
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0606779104
Emergence of tempered preferential attachment from optimization
Abstract
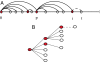
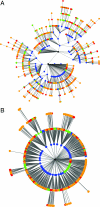
We show how preferential attachment can emerge in an optimization framework, resolving a long-standing theoretical controversy. We also show that the preferential attachment model so obtained has two novel features, saturation and viability, which have natural interpretations in the underlying network and lead to a power-law degree distribution with exponential cutoff. Moreover, we consider a generalized version of this preferential attachment model with independent saturation and viability, leading to a broader class of power laws again with exponential cutoff. We present a collection of empirical observations from social, biological, physical, and technological networks, for which such degree distributions give excellent fits. We suggest that, in general, optimization models that give rise to preferential attachment with saturation and viability effects form a good starting point for the analysis of many networks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Mandelbrot B. Jackson W. Communication Theory. London: Butterworth; 1953. pp. 486–502.
-
- Carlson JM, Doyle J. Phys Rev E. 1999;60:1412–1427. - PubMed
-
- Fabrikant A, Koutsoupias E, Papadimitriou CH. Lect Notes Comp Sci (ICALP 2002) 2002;2380:110–122.
-
- Li L, Alderson D, Willinger W, Doyle J. ACM SIGCOMM Comp Comm Rev. 2004;34:3–14.
-
- Mahadevan P, Krioukov D, Fomenkov M, Huffaker B, Dimitropoulos X, claffy kc, Vahdat A. 2005 arxiv:cs.NI/0508033.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

