Type III effector activation via nucleotide binding, phosphorylation, and host target interaction
- PMID: 17397263
- PMCID: PMC1839166
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.0030048
Type III effector activation via nucleotide binding, phosphorylation, and host target interaction
Erratum in
- PLoS Pathog. 2007 Jun;3(6):e90
Abstract
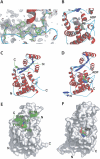
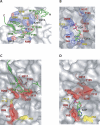
The Pseudomonas syringae type III effector protein avirulence protein B (AvrB) is delivered into plant cells, where it targets the Arabidopsis RIN4 protein (resistance to Pseudomonas maculicula protein 1 [RPM1]-interacting protein). RIN4 is a regulator of basal host defense responses. Targeting of RIN4 by AvrB is recognized by the host RPM1 nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat disease resistance protein, leading to accelerated defense responses, cessation of pathogen growth, and hypersensitive host cell death at the infection site. We determined the structure of AvrB complexed with an AvrB-binding fragment of RIN4 at 2.3 A resolution. We also determined the structure of AvrB in complex with adenosine diphosphate bound in a binding pocket adjacent to the RIN4 binding domain. AvrB residues important for RIN4 interaction are required for full RPM1 activation. AvrB residues that contact adenosine diphosphate are also required for initiation of RPM1 function. Nucleotide-binding residues of AvrB are also required for its phosphorylation by an unknown Arabidopsis protein(s). We conclude that AvrB is activated inside the host cell by nucleotide binding and subsequent phosphorylation and, independently, interacts with RIN4. Our data suggest that activated AvrB, bound to RIN4, is indirectly recognized by RPM1 to initiate plant immune system function.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Galán JE, Collmer A. Type III secretion machines: Bacterial devices for protein delivery into host cells. Science. 1999;284:1322–1328. - PubMed
-
- Mudgett MB. New insights to the function of phytopathogenic bacterial type III effectors in plants. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2005;56:509–531. - PubMed
-
- Grant SR, Fisher EJ, Chang JH, Mole BM, Dangl JL. Subterfuge and manipulation: Type III effector proteins of phytopathogenic bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 2006;60:425–449. - PubMed
-
- Dangl JL, Jones JDG. Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature. 2001;411:826–833. - PubMed
-
- Chisholm ST, Coaker G, Day B, Staskawicz BJ. Host-microbe interactions: Shaping the evolution of the plant immune response. Cell. 2006;124:803–814. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

