Improving hand function in stroke survivors: a pilot study of contralaterally controlled functional electric stimulation in chronic hemiplegia
- PMID: 17398254
- PMCID: PMC3961574
- DOI: 10.1016/j.apmr.2007.01.003
Improving hand function in stroke survivors: a pilot study of contralaterally controlled functional electric stimulation in chronic hemiplegia
Abstract
Objective: To assess the feasibility of a new stroke rehabilitation therapy for the hemiparetic hand.
Design: Case series. Pre- and postintervention assessment with 1- and 3-month follow-ups.
Setting: Clinical research laboratory of a large public hospital.
Participants: Three subjects with chronic (>6mo postcerebrovascular accident) upper-extremity hemiplegia.
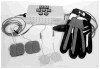
Intervention: Subjects used an electric stimulator to cause the paretic hand extensor muscles to contract and thereby open the hand. Subjects controlled the intensity of the stimulation, and thus the degree of hand opening, by volitionally opening the unimpaired contralateral hand, which was detected by an instrumented glove. For 6 weeks, subjects used the stimulator to perform active repetitive hand-opening exercises 2 hours daily at home and functional tasks 1.5 hours twice a week in the laboratory.
Main outcome measures: Maximum voluntary finger extension, maximum voluntary isometric finger-extension moment, finger-movement control, and box and block test (BBT) score at pre- and posttreatment and at 1 month and 3 months posttreatment.
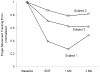
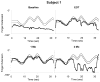
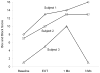
Results: Maximum voluntary finger extension increased from baseline to end of treatment and from the end of treatment to 1-month follow-up in 2 subjects. Maximum voluntary isometric finger-extension moment, finger-movement control, and BBT score increased from baseline to the end of treatment and from the end of treatment to 1-month follow-up in all 3 subjects. The improvements generally declined at 3 months.
Conclusions: The results suggest a positive effect on motor impairment, meriting further investigation of the intervention.
Figures


References
-
- Lai SM, Studenski S, Duncan PW, Perera S. Persisting consequences of stroke measured by the Stroke Impact Scale. Stroke. 2002;33:1840–1844. - PubMed
-
- Parker VM, Wade DT, Langton Hewer R. Loss of arm function after stroke: measurement, frequency, and recovery. Int Rehabil Med. 1986;8:69–73. - PubMed
-
- Jorgensen HS, Nakayama H, Raaschou HO, Vive-Larsen J, Stoier M, Olsen TS. Outcome and time course of recovery in stroke. Part II: Time course of recovery. The Copenhagen Stroke Study. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 1995;76:406–412. - PubMed
-
- Duncan PW, Goldstein LB, Matchar D, Divine GW, Feussner J. Measurement of motor recovery after stroke. Outcome assessment and sample size requirements. Stroke. 1992;23:1084–1089. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

