Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase and stimulation of Akt kinase signaling pathways: Two approaches with therapeutic potential in the treatment of neurodegenerative disease
- PMID: 17399794
- PMCID: PMC1964795
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.02.002
Inhibition of mitogen-activated protein kinase and stimulation of Akt kinase signaling pathways: Two approaches with therapeutic potential in the treatment of neurodegenerative disease
Abstract
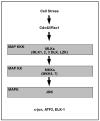
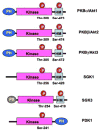
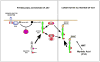
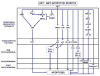
The neurodegenerative diseases of adulthood, including Alzheimer's disease (AD) and Parkinson's disease (PD), pose an enormous and growing public health burden. Although effective symptomatic treatments exist for PD, and, to a lesser extent, for AD, there is no therapy for these disorders which will forestall their progression. With the rise of the concept of programmed cell death (PCD) came the realization that even in the absence of complete knowledge of proximate causes neuroprotection may nevertheless be possible by targeting the pathways of PCD. One set of signaling pathways that have been implicated in cell death are the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathways. The possibility of blocking these pathways and thereby providing neuroprotection has recently been put to the test in a clinical trial of a mixed lineage kinase inhibitor in the treatment of PD. Unfortunately, this trial failed to demonstrate a protective effect. Based on considerations related to the implementation of the trial, it would be premature to conclude that inhibition of MAPK signaling is a failed strategy. In spite of these negative results, the MAPK and related kinase pathways retain their importance as potential targets in PD. In relation to pathogenesis, the discovery of mutations in the mixed lineage kinase (MLK)-like kinase leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) suggests a role for these kinases in regulating the viability of dopamine neurons. In relation to treatment, the survival signaling kinase Akt has been demonstrated in vivo to mediate striking neurotrophic and antiapoptotic effects. Thus, it is likely that therapeutic targets related to these kinase signaling pathways will emerge.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Mixed lineage kinase-c-jun N-terminal kinase signaling pathway: a new therapeutic target in Parkinson's disease.Mov Disord. 2005 Jun;20(6):653-64. doi: 10.1002/mds.20390. Mov Disord. 2005. PMID: 15719422 Review.
-
Discovery of CEP-1347/KT-7515, an inhibitor of the JNK/SAPK pathway for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases.Prog Med Chem. 2002;40:23-62. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6468(08)70081-x. Prog Med Chem. 2002. PMID: 12516522 Review.
-
Response of non-small cell lung cancer cells to the inhibitors of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt- and MAPK kinase 4/c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase pathways: an effective therapeutic strategy for lung cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2005 Aug 15;11(16):6065-74. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0009. Clin Cancer Res. 2005. PMID: 16115952
-
Neurotrophic effects of a cyanine dye via the PI3K-Akt pathway: attenuation of motor discoordination and neurodegeneration in an ataxic animal model.PLoS One. 2011 Feb 11;6(2):e17137. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0017137. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21347252 Free PMC article.
-
Understanding Abnormal c-JNK/p38MAPK Signaling Overactivation Involved in the Progression of Multiple Sclerosis: Possible Therapeutic Targets and Impact on Neurodegenerative Diseases.Neurotox Res. 2021 Oct;39(5):1630-1650. doi: 10.1007/s12640-021-00401-6. Epub 2021 Aug 25. Neurotox Res. 2021. PMID: 34432262 Review.
Cited by
-
Akt1 mediates neuronal differentiation in zebrafish via a reciprocal interaction with notch signaling.PLoS One. 2013;8(1):e54262. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0054262. Epub 2013 Jan 14. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23342113 Free PMC article.
-
The second generation mixed lineage kinase-3 (MLK3) inhibitor CLFB-1134 protects against neurotoxin-induced nigral dopaminergic neuron loss.Exp Neurol. 2019 Aug;318:157-164. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2019.05.002. Epub 2019 May 8. Exp Neurol. 2019. PMID: 31077715 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the LRRK2 gene in Parkinsonism.Mol Neurodegener. 2014 Nov 12;9:47. doi: 10.1186/1750-1326-9-47. Mol Neurodegener. 2014. PMID: 25391693 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Drosophila hep pathway mediates Lrrk2-induced neurodegeneration.Biochem Cell Biol. 2018 Aug;96(4):441-449. doi: 10.1139/bcb-2017-0262. Epub 2017 Dec 21. Biochem Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29268033 Free PMC article.
-
Fenobam promoted the neuroprotective effect of PEP-1-FK506BP following oxidative stress by increasing its transduction efficiency.BMB Rep. 2013 Nov;46(11):561-6. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2013.46.11.080. BMB Rep. 2013. PMID: 24152913 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Anderson AJ, Cummings BJ, Cotman CW. Increased immunoreactivity for Jun- and Fos-related proteins in Alzheimer's disease: association with pathology. Exp Neurol. 1994;125:286–295. - PubMed
-
- Barthwal MK, Sathyanarayana P, Kundu CN, Rana B, Pradeep A, Sharma C, et al. Negative regulation of mixed lineage kinase 3 by protein kinase B/AKT leads to cell survival. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:3897–3902. - PubMed
-
- Bayascas JR, Alessi DR. Regulation of Akt/PKB Ser473 phosphorylation. Mol Cell. 2005;18:143–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

