A colorimetric assay method to measure acetyl-CoA synthetase activity: application to woodchuck model of hepatitis virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 17399795
- PMCID: PMC1995416
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jbbm.2007.02.008
A colorimetric assay method to measure acetyl-CoA synthetase activity: application to woodchuck model of hepatitis virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
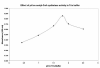
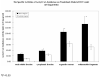
A new spectrophotometric method for quantitation of acetyl-CoA synthetase (ACAS) activity is developed. It has been applied for ACAS assay in the liver tissues of a woodchuck model of hepatitis virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The assay is based on the established pyrophosphate (PPi) detection system. ACAS activity is indexed by the amount of PPi, the product of ACAS reaction system of activated form of acetate (acetyl-CoA) with ACAS catalysis. PPi is determined quantitatively as the amount of chromophore formed with molybdate reagent, 1-amino-2-naphthol-4-sulfonic acid in bisulfite and 2-mercaptoethanol. PPi reacts with molybdate reagent to produce phosphomolybdate and PPi-molybdate complexes. 2-mercaptoethanol is responsible for color formation which has the peak absorbance at 580 nm. This method was sensitive from 1 to 20 nmol of PPi in a 380-mul sample (1-cm cuvette). A ten-fold excess of Pi did not interfere with the determination of PPi. To study the major metabolic pathways of imaging tracer [1-(11)C]-acetate in tumors for detection of HCC by Positron Emission Tomography (PET), the activity of one of the key enzymes involved in acetate or [1-(11)C]-acetate metabolism, ACAS was assayed by this newly developed assay in the tissue samples of woodchuck HCCs. A significant increase of ACAS activity was observed in the liver tissues of woodchuck HCCs as compared with neighboring regions surrounding the tumors (P<0.05). The respective ACAS activities in the subcellular locations were also significantly higher in HCCs than in the surrounding tissues (P<0.05) (total soluble fraction: 876.61+/-34.64 vs. 361.62+/-49.97 mU/g tissue; cytoplasmic fraction: 1122.02+/-112.39 vs. 732.32+/-84.44 mU/g tissue; organelle content: 815.79+/-100.77 vs. 547.91+/-97.05 mU/ g tissue; sedimentable fragment: 251.92+/-51.56 vs. 90.94+/-18.98 mU/ g tissue). The finding suggests an increase in ACAS activity in the liver cancer of woodchuck models of HCC as compared to that in the normal woodchuck liver. The developed assay is rapid, simple and accurate and is suitable for the investigation of ACAS activity under physiologic and pathophysiologic conditions.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Hexokinase and glucose-6-phosphatase activity in woodchuck model of hepatitis virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma.Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006 Jun;143(2):225-31. doi: 10.1016/j.cbpc.2006.02.005. Epub 2006 Mar 6. Comp Biochem Physiol C Toxicol Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16581304
-
PET imaging of hepatocellular carcinoma with 2-deoxy-2[18F]fluoro-D-glucose, 6-deoxy-6[18F] fluoro-D-glucose, [1-11C]-acetate and [N-methyl-11C]-choline.Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009 Apr;53(2):144-56. Epub 2008 Nov 28. Q J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2009. PMID: 19039303
-
Cross-species hybridization of woodchuck hepatitis virus-induced hepatocellular carcinoma using human oligonucleotide microarrays.World J Gastroenterol. 2006 Aug 7;12(29):4646-51. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v12.i29.4646. World J Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16937433 Free PMC article.
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma in the woodchuck model of hepatitis B virus infection.Gastroenterology. 2004 Nov;127(5 Suppl 1):S283-93. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.09.043. Gastroenterology. 2004. PMID: 15508096 Review.
-
The woodchuck model of hepatitis B virus infection.ILAR J. 2001;42(2):89-102. doi: 10.1093/ilar.42.2.89. ILAR J. 2001. PMID: 11406711 Review.
Cited by
-
Acetate activation in Methanosaeta thermophila: characterization of the key enzymes pyrophosphatase and acetyl-CoA synthetase.Archaea. 2012;2012:315153. doi: 10.1155/2012/315153. Epub 2012 Aug 15. Archaea. 2012. PMID: 22927778 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of fasting on PET Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Cancer Ther. 2013 Apr;4(2):561-567. doi: 10.4236/jct.2013.42071. J Cancer Ther. 2013. PMID: 24683497 Free PMC article.
-
PET Imaging of Hepatocellular Carcinoma Using ZD2-(68Ga-NOTA).J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023 Feb 22;10:291-301. doi: 10.2147/JHC.S390939. eCollection 2023. J Hepatocell Carcinoma. 2023. PMID: 36860804 Free PMC article.
-
Both forward and reverse TCA cycles operate in green sulfur bacteria.J Biol Chem. 2010 Nov 12;285(46):35848-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.157834. Epub 2010 Jul 22. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20650900 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a transcreener assay for detection of AMP- and GMP-producing enzymes.Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2010 Jun;8(3):344-55. doi: 10.1089/adt.2009.0254. Assay Drug Dev Technol. 2010. PMID: 20158441 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Stern JR, Shapiro B, Stadtman ER, Ochoa SJ. Enzymatic synthesis of citric acid. III. Reversibility and mechanism. J Biol Chem. 1951;193:703–720. - PubMed
-
- Aas M, Brener J. Short-chain fatty acid activation in rat liver. A new assay procedure for the enzymes and studies on their intracellular localization. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1968;164:157–166. - PubMed
-
- Upson RH, Haugland RP, Malekzadeh MN, Haugland RP. A spectrophotometric method to measure enzymatic activity in reactions that generate inorganic pyrophosphate. Anal Biochem. 1996;243:41–45. - PubMed
-
- Huang KP. A sensitive assay method of acetyl CoA sythetase. Anal Biochem. 1970;37:98–104. - PubMed
-
- Putinins RF, Yamada EW. Colorimetric determination of inorganic pyrophosphate by a manual or automated method. Anal Biochem. 1975;68:185–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

