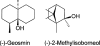Biochemical and ecological control of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in source waters
- PMID: 17400777
- PMCID: PMC1932821
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.02250-06
Biochemical and ecological control of geosmin and 2-methylisoborneol in source waters
Figures
References
-
- Aoyama, K., B. I. Tomita, and K. Chaya. 1993. Influence of incubation temperature on production of earthy-musty odour substances by actinomycetes. Jpn. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health 39:207-212.
-
- Baker, P. D., D. A. Steffensen, A. R. Humpage, B. C. Nicholson, I. R. Falconer, B. Lanthois, K. M. Fergusson, and C. P. Saint. 2001. Preliminary evidence of toxicity associated with the benthic cyanobacterium Phormidium in South Australia. Environ. Toxicol. 16:506-511. - PubMed
-
- Baum, D. 1992. Phylogenetic species concepts. TREE 7:1-3. - PubMed
-
- Bentley, R., and R. Meganathan. 1981. Geosmin and methylisoborneol biosynthesis in streptomycetes. Evidence for an isoprenoid pathway and its absence in non-differentiating isolates. FEBS Lett. 125:220-222. - PubMed
-
- Bowmer, K. H., A. Padovan, R. L. Oliver, W. Korth, and G. G. Ganf. 1992. Physiology of geosmin production by Anabaena circinalis isolated from the Murrumbidgee River, Australia. Water Sci. Technol. 25:259-267.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources