Purification and crystallization of Vibrio fischeri CcdB and its complexes with fragments of gyrase and CcdA
- PMID: 17401216
- PMCID: PMC2330220
- DOI: 10.1107/S1744309107012092
Purification and crystallization of Vibrio fischeri CcdB and its complexes with fragments of gyrase and CcdA
Abstract
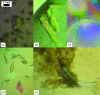
The ccd toxin-antitoxin module from the Escherichia coli F plasmid has a homologue on the Vibrio fischeri integron. The homologue of the toxin (CcdB(Vfi)) was crystallized in two different crystal forms. The first form belongs to space group I23 or I2(1)3, with unit-cell parameter a = 84.5 A, and diffracts to 1.5 A resolution. The second crystal form belongs to space group C2, with unit-cell parameters a = 58.5, b = 43.6, c = 37.5 A, beta = 110.0 degrees, and diffracts to 1.7 A resolution. The complex of CcdB(Vfi) with the GyrA14(Vfi) fragment of V. fischeri gyrase crystallizes in space group P2(1)2(1)2(1), with unit-cell parameters a = 53.5, b = 94.6, c = 58.1 A, and diffracts to 2.2 A resolution. The corresponding mixed complex with E. coli GyrA14(Ec) crystallizes in space group C2, with unit-cell parameters a = 130.1, b = 90.8, c = 58.1 A, beta = 102.6 degrees, and diffracts to 1.95 A. Finally, a complex between CcdB(Vfi) and part of the F-plasmid antitoxin CcdA(F) crystallizes in space group P2(1)2(1)2(1), with unit-cell parameters a = 46.9, b = 62.6, c = 82.0 A, and diffracts to 1.9 A resolution.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Structural and thermodynamic characterization of Vibrio fischeri CcdB.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 19;285(8):5606-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.068429. Epub 2009 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19959472 Free PMC article.
-
Alternative interactions define gyrase specificity in the CcdB family.Mol Microbiol. 2012 Jun;84(5):965-78. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2012.08069.x. Epub 2012 May 14. Mol Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22582791
-
Crystallization of the C-terminal domain of the addiction antidote CcdA in complex with its toxin CcdB.Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2005 Oct 1;61(Pt 10):949-52. doi: 10.1107/S1744309105029258. Epub 2005 Sep 30. Acta Crystallogr Sect F Struct Biol Cryst Commun. 2005. PMID: 16511204 Free PMC article.
-
Sequence-specific 1H, 15N and 13C resonance assignments of the 23.7-kDa homodimeric toxin CcdB from Vibrio fischeri.Biomol NMR Assign. 2009 Jun;3(1):145-7. doi: 10.1007/s12104-009-9161-9. Epub 2009 Apr 3. Biomol NMR Assign. 2009. PMID: 19636967
-
Molecular interactions of the CcdB poison with its bacterial target, the DNA gyrase.Int J Med Microbiol. 2002 Feb;291(6-7):537-44. doi: 10.1078/1438-4221-00164. Int J Med Microbiol. 2002. PMID: 11890555 Review.
Cited by
-
Structural and thermodynamic characterization of Vibrio fischeri CcdB.J Biol Chem. 2010 Feb 19;285(8):5606-13. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.068429. Epub 2009 Dec 2. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19959472 Free PMC article.
-
Vibrio cholerae ParE2 poisons DNA gyrase via a mechanism distinct from other gyrase inhibitors.J Biol Chem. 2010 Dec 17;285(51):40397-408. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.138776. Epub 2010 Oct 15. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 20952390 Free PMC article.
-
In front of and behind the replication fork: bacterial type IIA topoisomerases.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010 Jun;67(12):2001-24. doi: 10.1007/s00018-010-0299-5. Epub 2010 Feb 18. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2010. PMID: 20165898 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bahassi, E. M., Salmon, M. A., Van Melderen, L., Bernard, P. & Couturier, M. (1995). Mol. Microbiol.15, 1031–1037. - PubMed
-
- Bernard, P. & Couturier, M. (1992). J. Mol. Biol.226, 735–745. - PubMed
-
- Bernard, P., Kezdy, K. E., Van Melderen, L., Steyaert, J., Wyns, L., Pato, M. L., Higgins, P. N. & Couturier, M. (1993). J. Mol. Biol.234, 534–541. - PubMed
-
- Buts, L., Lah, J., Dao-Thi, M.-H., Wyns, L. & Loris, R. (2005). Trends Biochem. Sci.30, 672–679. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

