Gene expression profiling of chemically induced rat bladder tumors
- PMID: 17401461
- PMCID: PMC1838579
- DOI: 10.1593/neo.06814
Gene expression profiling of chemically induced rat bladder tumors
Abstract
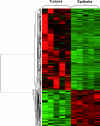
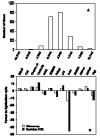
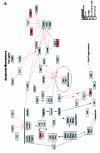
A variety of genetic alterations and gene expression changes are involved in the pathogenesis of bladder tumors. To explore expression changes in 4-hydroxybutyl(butyl)nitrosamine-induced rat bladder tumors, microarray analysis was performed. Analysis yielded 1,138 known genes and 867 expressed sequence tags that were changed when comparing tumors to normal rat epithelia. Altered genes included cell cycle-related genes, EGFR-Ras signaling genes, apoptosis genes, growth factors, and oncogenes. Using the pathway visualization tool GenMAPP, we found that these genes can be grouped along several pathways that control apoptosis, cell cycle, and integrin-mediated cell adhesion. When comparing current data with previous mouse bladder tumor data, we found that > 280 of the same known genes were differentially expressed in both mouse and rat bladder tumors, including cell cycle-related genes, small G proteins, apoptosis genes, oncogenes, tumor-suppressor genes, and growth factors. These results suggest that multiple pathways are involved in rat bladder tumorigenesis, and a common molecular mechanism was found in both rat and mouse bladder tumors.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Altered gene expression profile in mouse bladder cancers induced by hydroxybutyl(butyl)nitrosamine.Neoplasia. 2004 Sep-Oct;6(5):569-77. doi: 10.1593/neo.04223. Neoplasia. 2004. PMID: 15548366 Free PMC article.
-
Modulation of gene expression and cell-cycle signaling pathways by the EGFR inhibitor gefitinib (Iressa) in rat urinary bladder cancer.Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012 Feb;5(2):248-59. doi: 10.1158/1940-6207.CAPR-10-0363. Epub 2011 Oct 7. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2012. PMID: 21982874
-
Identification of differently expressed genes in chemical carcinogen-induced rat bladder cancers.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2009 Apr;29(2):220-6. doi: 10.1007/s11596-009-0217-y. Epub 2009 Apr 28. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2009. PMID: 19399409
-
H-ras activation and ras p21 expression in bladder tumors induced in F344/NCr rats by N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine.Carcinogenesis. 1990 Dec;11(12):2233-8. doi: 10.1093/carcin/11.12.2233. Carcinogenesis. 1990. PMID: 2265474
-
Bladder cancer. I. Molecular and genetic basis of carcinogenesis.Eur Urol. 2001 May;39(5):491-7. doi: 10.1159/000052494. Eur Urol. 2001. PMID: 11464028 Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of pathways involved in the processing of cancer and microenvironment information in MCA + TPA transformed C3H/10T1/2 cells.In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2013 Apr;49(4):295-305. doi: 10.1007/s11626-013-9593-5. Epub 2013 Mar 22. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2013. PMID: 23519560
-
Chemoprevention of BBN-Induced Bladder Carcinogenesis by the Selective Estrogen Receptor Modulator Tamoxifen.Transl Oncol. 2013 Jun 1;6(3):244-55. doi: 10.1593/tlo.13247. Print 2013 Jun. Transl Oncol. 2013. PMID: 23730403 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular credentialing of rodent bladder carcinogenesis models.Neoplasia. 2008 Aug;10(8):838-46. doi: 10.1593/neo.08432. Neoplasia. 2008. PMID: 18670642 Free PMC article.
-
Knockdown of Ki-67 by dicer-substrate small interfering RNA sensitizes bladder cancer cells to curcumin-induced tumor inhibition.PLoS One. 2012;7(11):e48567. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0048567. Epub 2012 Nov 12. PLoS One. 2012. PMID: 23152782 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin-A Viable Agent for Better Bladder Cancer Treatment.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 May 26;21(11):3761. doi: 10.3390/ijms21113761. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32466578 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Amling CL. Diagnosis and management of superficial bladder cancer. Curr Probl Cancer. 2001;25:219–278. - PubMed
-
- Brandau S, Bohle A. Bladder cancer: I. Molecular and genetic basis of carcinogenesis. Eur Urol. 2001;39:491–497. - PubMed
-
- Grubbs CJ, Lubet RA, Koki AT, Leahy KM, Masferrer JL, Steele VE, Kelloff GJ, Hill DL, Seibert K. Celecoxib inhibits N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)-nitrosamine-induced urinary bladder cancers in male B6D2F1 mice and female Fischer-344 rats. Cancer Res. 2000;60:5599–5602. - PubMed
-
- Grubbs CJ, Moon RC, Squire RA, Farrow GM, Stinson SF, Goodman DG, Brown CC, Sporn MB. 13-cis-Retinoic acid: inhibition of bladder carcinogenesis induced in rats by N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine. Science. 1977;198:743–744. - PubMed
-
- Ogawa K, Uzvolgyi E, St John MK, de Oliveira ML, Arnold L, Cohen SM. Frequent p53 mutations and occasional loss of chromosome 4 in invasive bladder carcinoma induced by N-butyl-N-(4-hydroxybutyl)nitrosamine in B6D2F1 mice. Mol Carcinog. 1998;21:70–79. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
