Arachidonic acid metabolism in brain physiology and pathology: lessons from genetically altered mouse models
- PMID: 17403135
- PMCID: PMC2084377
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.2007.04558.x
Arachidonic acid metabolism in brain physiology and pathology: lessons from genetically altered mouse models
Abstract
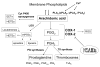
The arachidonic acid (AA) cascade involves the release of AA from the membrane phospholipids by a phospholipase A(2), followed by its subsequent metabolism to bioactive prostanoids by cyclooxygenases coupled with terminal synthases. Altered brain AA metabolism has been implicated in neurological, neurodegenerative, and psychiatric disorders. The development of genetically altered mice lacking specific enzymes of the AA cascade has helped to elucidate the individual roles of these enzymes in brain physiology and pathology. The roles of AA and its metabolites in brain physiology, with a particular emphasis on the phospholipase A(2)/cyclooxygenases pathway, are summarized, and the specific phenotypes of genetically altered mice relevant to brain physiology and neurotoxic models are discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmad AS, Saleem S, Ahmad M, Dore S. Prostaglandin EP1 receptor contributes to excitotoxicity and focal ischemic brain damage. Toxicol Sci. 2006;89:265–270. - PubMed
-
- Akaike A, Kaneko S, Tamura Y, Nakata N, Shiomi H, Ushikubi F, Narumiya S. Prostaglandin E2 protects cultured cortical neurons against N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-mediated glutamate cytotoxicity. Brain Res. 1994;663:237–243. - PubMed
-
- Almer G, Guegan C, Teismann P, Naini A, Rosoklija G, Hays AP, Chen C, Przedborski S. Increased expression of the proinflammatory enzyme cyclooxygenase-2 in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann Neurol. 2001;49:176–185. - PubMed
-
- Baile CA, Simpson CW, Bean SM, McLaughlin CL, Jacobs HL. Prostaglandins and food intake of rats: a component of energy balance regulation? Physiol Behav. 1973;10:1077–1085. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

