Glucose mediates the translocation of NeuroD1 by O-linked glycosylation
- PMID: 17403669
- PMCID: PMC2096475
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M701762200
Glucose mediates the translocation of NeuroD1 by O-linked glycosylation
Abstract
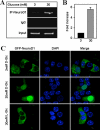
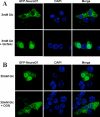
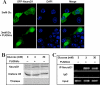
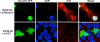
O-Linked GlcNAc modification of nuclear and cytosolic proteins has been shown to regulate the function of many cellular proteins. Increased O-linked glycosylation, observed under chronic hyperglycemia conditions, has been implicated in the pathogenesis of diabetes. However, the exact role of O-GlcNAc modification in regulating glucose homeostasis remains to be established. We report here that the subcellular localization of the pancreatic beta cell-specific transcription factor NeuroD1 is regulated by O-linked glycosylation in the mouse insulinoma cell line MIN6. Under low glucose conditions, NeuroD1 is mainly in the cytosol. However, treatment of MIN6 cells with high glucose results in O-linked GlcNAc modification of NeuroD1 and its subsequent translocation into the nucleus. Consistent with these data, treatment of MIN6 cells with O-(2-acetamido-2-deoxy-d-glucopyranosylidene)-amino N-phenylcarbamate, an inhibitor of O-GlcNAcase, causes Neuro-D1 localization to the nucleus and induction of insulin gene expression even on low glucose. Furthermore, we demonstrate that NeuroD1 interacts with the O-GlcNAc transferase, OGT only at high concentrations of glucose and depletion of OGT by using small interfering RNA oligos interferes with the nuclear localization of NeuroD1 on high glucose. On low glucose NeuroD1 interacts with the O-GlcNAcase and becomes deglycosylated, which is likely to be important for export of Neuro-D1 into cytosol in the presence of low glucose. In summary, the presented data suggest that glucose regulates the subcellular localization of NeuroD1 in pancreatic beta cells via O-linked GlcNAc modification of NeuroD1 by OGT.
Figures


References
-
- Permutt MA, Kipnis DM. J. Biol. Chem. 1972;247:1194–1199. - PubMed
-
- Docherty K, Clark AR. FASEB J. 1994;8:20–27. - PubMed
-
- Melloul D, Marshak S, Cerasi E. Diabetologia. 2002;45:309–326. - PubMed
-
- Hui H, Perfetti R. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2002;146:129–141. - PubMed
-
- Naya FJ, Stellrecht CM, Tsai MJ. Genes Dev. 1995;15:1009–1019. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

