The microRNA miR-124 antagonizes the anti-neural REST/SCP1 pathway during embryonic CNS development
- PMID: 17403776
- PMCID: PMC1838526
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.1519107
The microRNA miR-124 antagonizes the anti-neural REST/SCP1 pathway during embryonic CNS development
Abstract
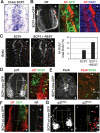
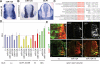
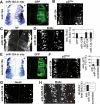
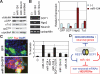
Neuronal gene expression is tightly regulated in developing CNS. Here, we demonstrate the anti-neural function of phosphatase SCP1 (small C-terminal domain phosphatase 1) during development. We further show that the neuron-enriched microRNA miR-124 directly targets SCP1-3' untranslated region (UTR) to suppress SCP1 expression. In developing spinal cord, expression of miR-124 and SCP1 is complementary, and miR-124 antagonism phenocopies SCP1 overexpression and vice versa. In P19 cells, miR-124 suppresses SCP1 expression and induces neurogenesis, and SCP1 counteracts this proneural activity of miR-124. Our results suggest that, during CNS development, timely down-regulation of SCP1 is critical for inducing neurogenesis, and miR-124 contributes to this process at least in part by down-regulating SCP1 expression.
Figures
References
-
- Alvarez-Garcia I., Miska E.A., Miska E.A. MicroRNA functions in animal development and human disease. Development. 2005;132:4653–4662. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Andres M.E., Burger C., Peral-Rubio M.J., Battaglioli E., Anderson M.E., Grimes J., Dallman J., Ballas N., Mandel G., Burger C., Peral-Rubio M.J., Battaglioli E., Anderson M.E., Grimes J., Dallman J., Ballas N., Mandel G., Peral-Rubio M.J., Battaglioli E., Anderson M.E., Grimes J., Dallman J., Ballas N., Mandel G., Battaglioli E., Anderson M.E., Grimes J., Dallman J., Ballas N., Mandel G., Anderson M.E., Grimes J., Dallman J., Ballas N., Mandel G., Grimes J., Dallman J., Ballas N., Mandel G., Dallman J., Ballas N., Mandel G., Ballas N., Mandel G., Mandel G. CoREST: A functional corepressor required for regulation of neural-specific gene expression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 1999;96:9873–9878. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ballas N., Battaglioli E., Atouf F., Andres M.E., Chenoweth J., Anderson M.E., Burger C., Moniwa M., Davie J.R., Bowers W.J., Battaglioli E., Atouf F., Andres M.E., Chenoweth J., Anderson M.E., Burger C., Moniwa M., Davie J.R., Bowers W.J., Atouf F., Andres M.E., Chenoweth J., Anderson M.E., Burger C., Moniwa M., Davie J.R., Bowers W.J., Andres M.E., Chenoweth J., Anderson M.E., Burger C., Moniwa M., Davie J.R., Bowers W.J., Chenoweth J., Anderson M.E., Burger C., Moniwa M., Davie J.R., Bowers W.J., Anderson M.E., Burger C., Moniwa M., Davie J.R., Bowers W.J., Burger C., Moniwa M., Davie J.R., Bowers W.J., Moniwa M., Davie J.R., Bowers W.J., Davie J.R., Bowers W.J., Bowers W.J., et al. Regulation of neuronal traits by a novel transcriptional complex. Neuron. 2001;31:353–365. - PubMed
-
- Ballas N., Grunseich C., Lu D.D., Speh J.C., Mandel G., Grunseich C., Lu D.D., Speh J.C., Mandel G., Lu D.D., Speh J.C., Mandel G., Speh J.C., Mandel G., Mandel G. REST and its corepressors mediate plasticity of neuronal gene chromatin throughout neurogenesis. Cell. 2005;121:645–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
