CD4+ lymphocytes and gamma interferon predominate in local immune responses in early experimental syphilis
- PMID: 17403876
- PMCID: PMC1932874
- DOI: 10.1128/IAI.01973-06
CD4+ lymphocytes and gamma interferon predominate in local immune responses in early experimental syphilis
Abstract
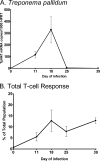
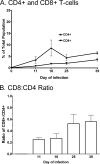
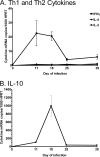
The clearance of Treponema pallidum subsp. pallidum from early syphilis lesions involves infiltration of a large number of mononuclear cells and is characteristic of a cell-mediated immune response. In the present study, we sought to determine the relative abundance of different T-lymphocyte populations and Th1/Th2-associated cytokines present in testicular lesions following experimental infection with the Chicago strain of T. pallidum. Using flow cytometry, we examined the proportion of CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells present throughout the progression and resolution of primary syphilis in the rabbit model. We related these findings to the results of real-time reverse transcription-PCR quantification of treponemal and cytokine mRNA levels. Treponemal mRNA levels reached peak values on day 18 postinfection, coincident with an initial peak in the level of T cells, which were primarily CD4(+) T cells. T-cell levels increased again during resolution of orchitis, and there was an increased proportion of CD8(+) T cells. The maximum gamma interferon (IFN-gamma) and interleukin-10 (IL-10) mRNA levels were observed on days 11 and 18, respectively, while only negligible amounts of IL-4 and IL-2 were detected throughout the infection. In addition to showing the temporal relationship between treponemal burden and T-cell responses during lesion progression, our results also demonstrate that the composition of the T-cell population changes during lesion resolution. The presence of the mRNA for IFN-gamma, but not IL-4, is consistent with cytokine expression in human syphilis and provides further support for the hypothesis that there is a Th1 predominance during the early immune response to T. pallidum.
Figures
References
-
- Baker-Zander, S. A., and S. A. Lukehart. 1992. Macrophage-mediated killing of opsonized Treponema pallidum. J. Infect. Dis. 165:69-74. - PubMed
-
- Bishop, N. H., and J. N. Miller. 1976. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis. II. The relationship of neutralizing factors in immune serum to acquired resistance. J. Immunol. 117:197-207. - PubMed
-
- Blanco, D. R., J. N. Miller, and P. A. Hanff. 1984. Humoral immunity in experimental syphilis: the demonstration of IgG as a treponemicidal factor in immune rabbit serum. J. Immunol. 133:2693-2697. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

