Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and biologic therapy: a medical revolution
- PMID: 17403952
- PMCID: PMC2600039
- DOI: 10.1136/pgmj.2006.052688
Immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) and biologic therapy: a medical revolution
Abstract
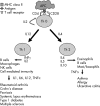
Targeted biologic therapies have revolutionised treatment of immune-mediated inflammatory diseases (IMIDs) due to their efficacy, speed of onset and tolerability. The discovery that clinically unrelated conditions, such as rheumatoid arthritis and Crohn's disease, share similar immune dysregulation has led to a shift in the management of IMIDs from one of organ-based symptom relief to mechanism-based treatment. The fact that anticytokine therapy has been effective in treating multiple orphan inflammatory conditions confirms the IMID paradigm. In this review we examine the biologic agents currently licensed for use in the US and Europe: infliximab, etanercept, adalimumab, rituximab, abatacept, anakinra, alefacept and efalizumab. We also discuss the rationale behind the management of IMIDs using rheumatoid arthritis, Crohn's disease, psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis as examples. For the medical profession, IMID represents a breakthrough in the way pathology is classified. In this burgeoning era of biologic therapy the prospect of complete disease remission is conceivable.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: Dr Annabel Kuek declares no conflicts of interest. Dr Andrew Östör and Dr Brian Hazleman receive sponsorship from Schering‐Plough, Wyeth, Abbott and Roche.
References
-
- Williams J P, Meyers J A. Immune‐mediated inflammatory disorders (I.M.I.D. s): the economic and clinical costs, Am J Manag Care 200221(Suppl)S664–S681. - PubMed
-
- Davidson A, Diamond B. Autoimmune diseases. N Engl J Med 2001345340–350. - PubMed
-
- Brophy S, Pavy S, Lewis P.et al Inflammatory eye, skin, and bowel disease in spondyloarthritis: genetic, phenotypic and environmental factors. J Rheumatol 2001282667–2673. - PubMed
-
- O'Shea J J, Ma A, Lipsky P. Cytokines and autoimmunity. Nat Immunol 2002237–45. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical