Regulation of ryanodine receptor-dependent calcium signaling by polycystin-2
- PMID: 17404231
- PMCID: PMC1851053
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0610324104
Regulation of ryanodine receptor-dependent calcium signaling by polycystin-2
Abstract
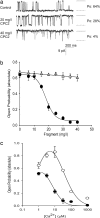
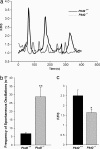
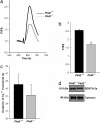
Mutations in polycystin-2 (PC2) cause autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease. A function for PC2 in the heart has not been described. Here, we show that PC2 coimmunoprecipitates with the cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR2) from mouse heart. Biochemical assays showed that the N terminus of PC2 binds the RyR2, whereas the C terminus only binds to RyR2 in its open state. Lipid bilayer electrophysiological experiments indicated that the C terminus of PC2 functionally inhibited RyR2 channel activity in the presence of calcium (Ca(2+)). Pkd2(-/-) cardiomyocytes had a higher frequency of spontaneous Ca(2+) oscillations, reduced Ca(2+) release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum stores, and reduced Ca(2+) content compared with Pkd2(+/+) cardiomyocytes. In the presence of caffeine, Pkd2(-/-) cardiomyocytes exhibited decreased peak fluorescence, a slower rate of rise, and a longer duration of Ca(2+) transients compared with Pkd2(+/+). These data suggest that PC2 is important for regulation of RyR2 function and that loss of this regulation of RyR2, as occurs when PC2 is mutated, results in altered Ca(2+) signaling in the heart.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
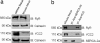

References
-
- Gabow PA, Grantham JJ. In: Diseases of the Kidney. Schrier RW, Gottschalk CW, editors. Boston: Little, Brown; 1997. pp. 535–569.
-
- Belz MM, Fick-Brosnahan GM, Hughes RL, Rubinstein D, Chapman AB, Johnson AM, McFann KK, Kaehny WD, Gabow PA. Kidney Int. 2003;63:1824–1830. - PubMed
-
- Chapman AB, Johnson AM, Rainguet S, Hossack K, Gabow P, Schrier RW. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1997;8:1292–1297. - PubMed
-
- Igarashi P, Somlo S. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2002;13:2384–2398. - PubMed
-
- Calvet JP. J Nephrol. 1998;11:24–34. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

