Continuous-wave Submillimeter-wave Gyrotrons
- PMID: 17404605
- PMCID: PMC1847421
- DOI: 10.1117/12.686436
Continuous-wave Submillimeter-wave Gyrotrons
Abstract
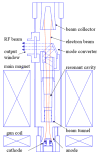
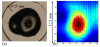
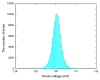
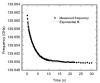
Recently, dynamic nuclear polarization enhanced nuclear magnetic resonance (DNP/NMR) has emerged as a powerful technique to obtain significant enhancements in spin spectra from biological samples. For DNP in modern NMR systems, a high power continuous-wave source in the submillimeter wavelength range is necessary. Gyrotrons can deliver tens of watts of CW power at submillimeter wavelengths and are well suited for use in DNP/NMR spectrometers. To date, 140 GHz and 250 GHz gyrotrons are being employed in DNP spectrometer experiments at 200 MHz and 380 MHz at MIT. A 460 GHz gyrotron, which has operated with 8 W of CW output power, will soon be installed in a 700 MHz NMR spectrometer. High power radiation with good spectral and spatial resolution from these gyrotrons should provide NMR spectrometers with high signal enhancement through DNP. Also, these tubes operating at submillimeter wavelengths should have important applications in research in physics, chemistry, biology, materials science and medicine.
Figures


References
-
- Sherwin MS, et al., editors. Opportunities in THz Science: Report of a DOE-NSF-NIH Workshop. Arlington; Feb, 2004.
-
- Sirtori C. Applied physics: Bridge for the Terahertz gap. Nature. May 2002;420(6912):131–133. - PubMed
-
- Becerra L, et al. Dynamic nuclear polarization with a cyclotron resonance maser at 5 T. Phys Rev Lett. 1993;71:5361–4. - PubMed
-
- Becerra L, et al. A Spectrometer for Dynamic Nuclear Polarization and Electron paramagnetic Resonance at High Frequencies. J Mag Res. 1995;117:28–40.
-
- Idehara T, et al. Development of frequency tunable, medium power gyrotrons (Gyrotron FU series) as submillimeter wave radiation sources”. IEEE Trans Plasma Sci. April 1999;27:340–354.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
