CD40Ig treatment results in allograft acceptance mediated by CD8CD45RC T cells, IFN-gamma, and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
- PMID: 17404623
- PMCID: PMC1839240
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI28801
CD40Ig treatment results in allograft acceptance mediated by CD8CD45RC T cells, IFN-gamma, and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase
Abstract
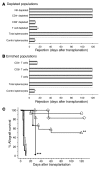
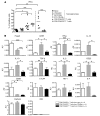
Treatment with CD40Ig results in indefinite allograft survival in a complete MHC-mismatched heart allograft model in the rat. Here we show that serial second, third, and fourth adoptive transfers of total splenocytes from CD40Ig-treated recipients into secondary recipients led to indefinite donor-specific allograft acceptance. Purification of splenocyte subpopulations from CD40Ig-treated recipients demonstrated that only the adoptively transferred CD8(+)CD45RC(low) subset resulted in donor-specific long-term survival, whereas CD8(+)CD45RC(low) T cells from naive animals did not. Accepted grafts displayed increased indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) expression restricted in the graft to ECs. Coculture of donor ECs with CD8(+)CD45RC(low) T cells purified from CD40Ig-treated animals resulted in donor-specific IDO expression dependent on IFN-gamma. Neutralization of IFN-gamma or IDO triggered acute allograft rejection in both CD40Ig-treated and adoptively transferred recipients. This study demonstrates for what we believe to be the first time that interference in CD40-CD40 ligand (CD40-CD40L) interactions induces allospecific CD8(+) Tregs that maintain allograft survival. CD8(+)CD45RC(low) T cells act through IFN-gamma production, which in turn induces IDO expression by graft ECs. Thus, donor alloantigen-specific CD8(+) Tregs may promote local graft immune privilege through IDO expression.
Figures





Comment in
-
Yin and yang interplay of IFN-gamma in inflammation and autoimmune disease.J Clin Invest. 2007 Apr;117(4):871-3. doi: 10.1172/JCI31860. J Clin Invest. 2007. PMID: 17404615 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Waldmann H., Cobbold S. Exploiting tolerance processes in transplantation. Science. 2004;305:209–212. - PubMed
-
- Wood K.J., Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells in transplantation tolerance. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2003;3:199–210. - PubMed
-
- Xystrakis E., et al. Identification of a novel natural regulatory CD8 T-cell subset and analysis of its mechanism of regulation. Blood. 2004;104:3294–3301. - PubMed
-
- Liu J., et al. Rat CD8+ FOXP3+ T suppressor cells mediate tolerance to allogeneic heart transplants, inducing PIR-B in APC and rendering the graft invulnerable to rejection. Transpl. Immunol. 2004;13:239–247. - PubMed
-
- Zhou J., Carr R.I., Liwski R.S., Stadnyk A.W., Lee T.D. Oral exposure to alloantigen generates intragraft CD8+ regulatory cells. J. Immunol. 2001;167:107–113. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

