Structural basis for ligand and heparin binding to neuropilin B domains
- PMID: 17405859
- PMCID: PMC1851056
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0700043104
Structural basis for ligand and heparin binding to neuropilin B domains
Abstract
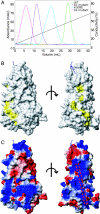
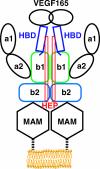
Neuropilin (Nrp) is a cell surface receptor with essential roles in angiogenesis and axon guidance. Interactions between Nrp and the positively charged C termini of its ligands, VEGF and semaphorin, are mediated by Nrp domains b1 and b2, which share homology to coagulation factor domains. We report here the crystal structure of the tandem b1 and b2 domains of Nrp-1 (N1b1b2) and show that they form a single structural unit. Cocrystallization of N1b1b2 with Tuftsin, a peptide mimic of the VEGF C terminus, reveals the site of interaction with the basic tail of VEGF on the b1 domain. We also show that heparin promotes N1b1b2 dimerization and map the heparin binding site on N1b1b2. These results provide a detailed picture of interactions at the core of the Nrp signaling complex and establish a molecular basis for the synergistic effects of heparin on Nrp-mediated signaling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Kolodkin AL, Levengood DV, Rowe EG, Tai YT, Giger RJ, Ginty DD. Cell. 1997;90:753–762. - PubMed
-
- He Z, Tessier-Lavigne M. Cell. 1997;90:739–751. - PubMed
-
- Soker S, Takashima S, Miao HQ, Neufeld G, Klagsbrun M. Cell. 1998;92:735–745. - PubMed
-
- Klagsbrun M, Takashima S, Mamluk R. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2002;515:33–48. - PubMed
-
- Takahashi T, Fournier A, Nakamura F, Wang LH, Murakami Y, Kalb RG, Fujisawa H, Strittmatter SM. Cell. 1999;99:59–69. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

