Dendritic patch-clamp recording
- PMID: 17406407
- PMCID: PMC7616975
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2006.164
Dendritic patch-clamp recording
Abstract
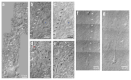
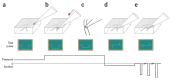
The patch-clamp technique allows investigation of the electrical excitability of neurons and the functional properties and densities of ion channels. Most patch-clamp recordings from neurons have been made from the soma, the largest structure of individual neurons, while their dendrites, which form the majority of the surface area and receive most of the synaptic input, have been relatively neglected. This protocol describes techniques for recording from the dendrites of neurons in brain slices under direct visual control. Although the basic technique is similar to that used for somatic patching, we describe refinements and optimizations of slice quality, microscope optics, setup stability and electrode approach that are required for maximizing the success rate for dendritic recordings. Using this approach, all configurations of the patch-clamp technique (cell-attached, inside-out, whole-cell, outside-out and perforated patch) can be achieved, even for relatively distal dendrites, and simultaneous multiple-electrode dendritic recordings are also possible. The protocol--from the beginning of slice preparation to the end of the first successful recording--can be completed in 3 h.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing financial interests.
Figures

References
-
- Llinas R, Nicholson C. Electrophysiological properties of dendrites and somata in alligator Purkinje cells. J Neurophysiol. 1971;34:532–551. - PubMed
-
- Stuart GJ, Dodt HU, Sakmann B. Patch-clamp recordings from the soma and dendrites of neurons in brain slices using infrared video microscopy. Pflugers Arch. 1993;423:511–518. - PubMed
-
- Stuart G, Häusser M. Initiation and spread of sodium action potentials in cerebellar Purkinje cells. Neuron. 1994;13:703–712. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

