Determination of the folding of proteins as a function of denaturants, osmolytes or ligands using circular dichroism
- PMID: 17406529
- PMCID: PMC2728349
- DOI: 10.1038/nprot.2006.229
Determination of the folding of proteins as a function of denaturants, osmolytes or ligands using circular dichroism
Abstract
Circular dichroism (CD) is an excellent tool for examining the interactions and stability of proteins. This protocol covers methods to obtain and analyze circular dichroism spectra to measure changes in the folding of proteins as a function of denaturants, osmolytes or ligands. Applications include determination of the free energy of folding of a protein, the effects of mutations on protein stability and the estimation of binding constants for the interactions of proteins with other proteins, DNA or ligands, such as substrates or inhibitors. The experiments require 2-5 h.
Figures

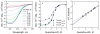

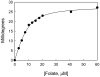
References
-
- Fowler VM, Greenfield NJ, Moyer J. Tropomodulin contains two actin filament pointed end-capping domains. J. Biol. Chem. 2003;278:40000–9. - PubMed
-
- Smith L, Greenfield NJ, Hitchcock-DeGregori SE. The effects of deletion of the amino-terminal helix on troponin C function and stability. J. Biol. Chem. 1994;269:9857–63. - PubMed
-
- Greenfield NJ, Williams MN, Poe M, Hoogsteen K. Circular dichroism studies of dihydrofolate reductase from a methotrexate-resistant strain of Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1972;11:4706–11. - PubMed
-
- Schellman JA. Macromolecular Binding. Biopolymers. 1975;14:999–1018.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

