Molecular genetics of the platelet serotonin system in first-degree relatives of patients with autism
- PMID: 17406648
- PMCID: PMC2739682
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.npp.1301406
Molecular genetics of the platelet serotonin system in first-degree relatives of patients with autism
Abstract
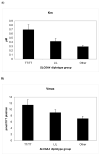
Elevated platelet serotonin (5-hydroxytryptamine, 5-HT) is found in a subset of children with autism and in some of their first-degree relatives. Indices of the platelet serotonin system, including whole blood 5-HT, 5-HT binding affinity for the serotonin transporter (K(m)), 5-HT uptake (V(max)), and lysergic acid diethylamide (LSD) receptor binding, were previously studied in 24 first-degree relatives of probands with autism, half of whom were selected for elevated whole blood 5-HT levels. All subjects were then genotyped for selected polymorphisms at the SLC6A4, HTR7, HTR2A, ITGB3, and TPH1 loci. Previous studies allowed an a priori prediction of SLC6A4 haplotypes that separated the subjects into three groups that showed significantly different 5-HT binding affinity (K(m), p=0.005) and 5-HT uptake rate (V(max), p=0.046). Genotypes at four individual polymorphisms in SLC6A4 were not associated with platelet 5-HT indices. Haplotypes at SLC6A4 and individual genotypes of polymorphisms at SLC6A4, HTR7, HTR2A, ITGB3, and TPH1 showed no significant association with whole blood 5-HT. Haplotype analysis of two polymorphisms in TPH1 revealed a nominally significant association with whole blood 5-HT (p=0.046). These initial studies of indices of the 5-HT system with several single-nucleotide polymorphisms at loci in this system generate hypotheses for testing in other samples.
Figures

References
-
- Abramson RK, Wright HH, Carpenter R, Brennan W, Lumpuy O, Cole E, Young SR. Elevated blood serotonin in autistic probands and their first-degree relatives. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 1989;19:397–407. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GM, Feibel FC, Cohen DJ. Determination of serotonin in whole blood, platelet-rich plasma, platelet-poor plasma and plasma ultrafiltrate. Life Sci. 1987;40:1063–1070. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GM, Gutknecht L, Cohen DJ, Brailly-Tabard S, Cohen JH, Ferrari P, et al. Serotonin transporter promoter variants in autism: functional effects and relationship to platelet hyperserotonemia. Mol Psychiatry. 2002;7:831–836. - PubMed
-
- Anderson GM, Young JG, Cohen DJ, Schlicht KR. Liquid-chromatographic determination of serotonin and tryptophan in whole blood and plasma. Clinical Chemistry. 1981;27:775–776. - PubMed
-
- Arora R, Meltzer H. A modified assay for determining serotonin uptake in human platelets. Clinical Chemistry Acta. 1981;112:225–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

