Enhanced fibrinolysis in fingerstick blood samples: a possible role for matrix metalloproteinase-9
- PMID: 17407789
- PMCID: PMC1995446
- DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2006.12.018
Enhanced fibrinolysis in fingerstick blood samples: a possible role for matrix metalloproteinase-9
Figures
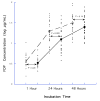
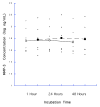
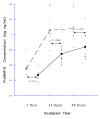
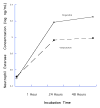
References
-
- Cesarman-Maus G, Hajjar KA. Molecular mechanisms of fibrinolysis. Br J Haematol. 2005;129:307–21. - PubMed
-
- Nagase H, Woessner JF. Matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1999;274:21491–4. - PubMed
-
- Lijnen HR. Matrix metalloproteinases and cellular fibrinolytic activity. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2002;67:107–15. - PubMed
-
- Horne MK, Merryman PK, Cullinane AM. Plasminogen interaction with platelets: the importance of carboxyterminal lysines. Thromb Res. 2005;116:499–507. - PubMed
-
- Horne M, Merryman P, Cullinane A, Hutchison K. Fibrinolysis in clots of blood obtained by fingerstick. Blood. 1997;90(suppl 1):96b.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

