basA regulates cell wall organization and asexual/sexual sporulation ratio in Aspergillus nidulans
- PMID: 17409079
- PMCID: PMC1893078
- DOI: 10.1534/genetics.106.068239
basA regulates cell wall organization and asexual/sexual sporulation ratio in Aspergillus nidulans
Abstract
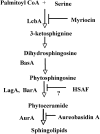
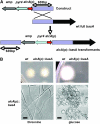
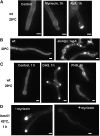
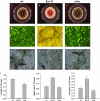
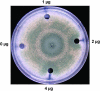
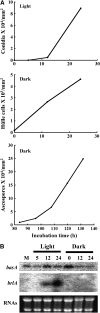
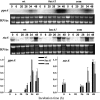
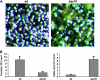
Sphingolipid C4 hydroxylase catalyzes the conversion of dihydrosphingosine to phytosphingosine. In Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Sur2 is essential for sphingolipid C4 hydroxylation activity but not essential for normal growth. Here we demonstrate that the Aspergillus nidulans Sur2 homolog BasA is also required for phytosphingosine biosynthesis but is also essential for viability. We previously reported that a point missense mutation in basA resulted in aberrant cell wall thickening. Here our data suggest that accumulation of dihydrosphingosine is responsible for this phenotype. In addition, two different mutations in basA consistently accelerated the transition from asexual development to sexual development compared to the wild-type strain. The phenotype could be suppressed by exogenous addition of phytosphingosine. Northern analysis suggests that faster sexual development in the basA mutant might be due to a higher transcription level of ppoA and steA, genes demonstrated to coordinate a balance between asexual and sexual development in A. nidulans. Consistent with these findings, mutations in the ceramide-synthase-encoding genes barA and lagA also caused faster transition from asexual to sexual development, supporting the involvement of sphingolipid metabolism in fungal morphogenesis.
Figures

References
-
- Adams, T. H., M. T. Boylan and W. E. Timberlake, 1988. brlA is necessary and sufficient to direct conidiophore development in Aspergillus nidulans. Cell 54: 353–362. - PubMed
-
- Bae, J. H., J. H. Sohn, C. S. Park, J. S. Rhee and E. S. Choi, 2004. Cloning and functional characterization of the SUR2/SYR2 gene encoding sphinganine hydroxylase in Pichia ciferrii. Yeast 21: 437–443. - PubMed
-
- Beeler, T., D. Bacikova, K. Gable, L. Hopkins, C. Johnson et al., 1998. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae TSC10/YBR265w gene encoding 3-ketosphinganine reductase is identified in a screen for temperature-sensitive suppressors of the Ca2+-sensitive csg2Delta mutant. J. Biol. Chem. 273: 30688–30694. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

