Identification of a novel C-terminal cleavage of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus PreGN that leads to generation of an NSM protein
- PMID: 17409136
- PMCID: PMC1900101
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02730-06
Identification of a novel C-terminal cleavage of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus PreGN that leads to generation of an NSM protein
Abstract
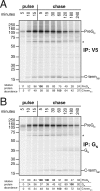
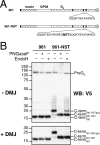
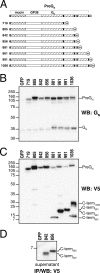
The structural glycoproteins of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus (CCHFV; genus Nairovirus, family Bunyaviridae) are derived through endoproteolytic cleavage of a 1,684-amino-acid M RNA segment-encoded polyprotein. This polyprotein is cotranslationally cleaved into the PreGN and PreGC precursors, which are then cleaved by SKI-1 and a SKI-1-like protease to generate the N termini of GN and GC, respectively. However, the resulting polypeptide defined by the N termini of GN and GC is predicted to be larger (58 kDa) than mature GN (37 kDa). By analogy to the topologically similar M segment-encoded polyproteins of viruses in the Orthobunyavirus genus, the C-terminal region of PreGN that contains four predicted transmembrane domains may also contain a nonstructural protein, NSM. To characterize potential PreGN C-terminal cleavage events, a panel of epitope-tagged PreGN truncation and internal deletion mutants was developed. These constructs allowed for the identification of a C-terminal endoproteolytic cleavage within, or very proximal to, the second predicted transmembrane domain following the GN ectodomain and the subsequent generation of a C-terminal fragment. Pulse-chase experiments showed that PreGN C-terminal cleavage occurred shortly after synthesis of the precursor and prior to generation of the GN glycoprotein. The resulting fragment trafficked to the Golgi compartment, the site of virus assembly. Development of an antiserum specific to the second cytoplasmic loop of PreGN allowed detection of cell-associated NSM proteins derived from transient expression of the complete CCHFV M segment and also in the context of virus infection.
Figures



References
-
- Ahmed, A. A., J. M. McFalls, C. Hoffmann, C. M. Filone, S. M. Stewart, J. Paragas, S. Khodjaev, D. Shermukhamedova, C. S. Schmaljohn, R. W. Doms, and A. Bertolotti-Ciarlet. 2005. Presence of broadly reactive and group-specific neutralizing epitopes on newly described isolates of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus. J. Gen. Virol. 86:3327-3336. - PubMed
-
- Bertolotti-Ciarlet, A., J. Smith, K. Strecker, J. Paragas, L. A. Altamura, J. M. McFalls, N. Frias-Staheli, A. Garcia-Sastre, C. S. Schmaljohn, and R. W. Doms. 2005. Cellular localization and antigenic characterization of Crimean-Congo hemorrhagic fever virus glycoproteins. J. Virol. 79:6152-6161. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cash, P. 1985. Polypeptide synthesis of Dugbe virus, a member of the Nairovirus genus of the Bunyaviridae. J. Gen. Virol. 66:141-148. - PubMed
-
- Clerx, J. P., and D. H. Bishop. 1981. Qalyub virus, a member of the newly proposed Nairovirus genus (Bunyavividae). Virology 108:361-372. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

