The cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+ T-cell response expands with age and markedly alters the CD4+ T-cell repertoire
- PMID: 17409149
- PMCID: PMC1933343
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.01262-06
The cytomegalovirus-specific CD4+ T-cell response expands with age and markedly alters the CD4+ T-cell repertoire
Abstract
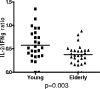
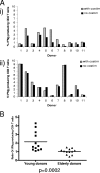
Immune function in the elderly is associated with a number of phenotypic and functional abnormalities, and this phenomenon of immune senescence is associated with increased susceptibility to infection. The immune response to pathogens frequently declines with age, but the CD8(+) T-cell response to cytomegalovirus (CMV) is unusual, as it demonstrates a significant expansion over time. Here we have documented the CD4(+) T-cell immune response to CMV in healthy donors of different ages. The magnitude of the CMV-specific CD4(+) T-cell immune response increases from a mean of 2.2% of the CD4(+) T-cell pool in donors below 50 years of age to 4.7% in donors aged over 65 years. In addition, CMV-specific CD4(+) T cells in elderly donors demonstrate decreased production of interleukin-2 and less dependence on costimulation. CMV seropositivity is associated with marked changes in the phenotype of the overall CD4(+) T-cell repertoire in healthy aged donors, including an increase in CD57(+) expression and a decrease in CD28 and CD27 expression, a phenotypic profile characteristic of immune senescence. This memory inflation of CMV-specific CD4(+) T cells contributes to evidence that CMV infection may be damaging to immune function in elderly individuals.
Figures


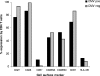
References
-
- Almanzar G., S. Schwaiger, B. Jenewein, M. Keller, D. Herndler-Brandstetter, R. Wurzner, D. Schonitzer, and B. Grubeck-Loebenstein. 2005. Long-term cytomegalovirus infection leads to significant changes in the composition of the CD8+ T-cell repertoire, which may be the basis for an imbalance in the cytokine production profile in elderly persons. J. Virol. 79:3675-3683. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andersson, E., M. Ohlin, C. A. Borrebaeck, and R. Carlsson. 1995. CD4+ CD57+ T cells derived from peripheral blood do not support immunoglobulin production by B cells. Cell. Immunol. 163:245-253. - PubMed
-
- Asanuma, H., M. Sharp, H. T. Maecker, V. C. Maino, and A. M. Arvin. 2000. Frequencies of memory T cells specific for varicella-zoster virus, herpes simplex virus, and cytomegalovirus by intracellular detection of cytokine expression. J. Infect. Dis. 181:859-866. - PubMed
-
- Baars, P. A., M. M. Maurice, M. Rep, B. Hooibrink, and R. A. van Lier. 1995. Heterogeneity of the circulating human CD4+ T cell population. Further evidence that the CD4+ CD45RA− CD27− T cell subset contains specialized primed T cells. J. Immunol. 154:17-25. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein, E., D. Kaye, E. Abrutyn, P. Gross, M. Dorfman, and D. M. Murasko. 1999. Immune response to influenza vaccination in a large healthy elderly population. Vaccine 17:82-94. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

