The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K5 E3 ubiquitin ligase modulates targets by multiple molecular mechanisms
- PMID: 17409151
- PMCID: PMC1900076
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02751-06
The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K5 E3 ubiquitin ligase modulates targets by multiple molecular mechanisms
Abstract
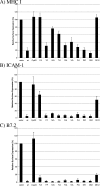
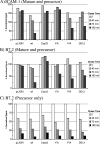
Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encodes two highly related membrane-associated, RING-CH-containing (MARCH) family E3 ubiquitin ligases, K3 and K5, that can down regulate a variety of cell surface proteins through enhancement of their endocytosis and degradation. In this report we present data that while K5 modulation of major histocompatibility complex class I (MHC-I) closely mirrors the mechanisms used by K3, alternative molecular pathways are utilized by this E3 ligase in the down regulation of intercellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) and B7.2. Internalization assays demonstrate that down regulation of each target can occur through increased endocytosis from the cell surface. However, mutation of a conserved tyrosine-based endocytosis motif in K5 resulted in a protein lacking the ability to direct an increased rate of MHC-I or ICAM-1 internalization but still able to down regulate B7.2 in a ubiquitin-dependent but endocytosis-independent manner. Further, mutation of two acidic clusters abolished K5-mediated MHC-I degradation while only slightly decreasing ICAM-1 or B7.2 protein destruction. This same mutant abolished detectable ubiquitylation of all targets. These data indicate that while K5 can act as an E3 ubiquitin ligase to directly mediate cell surface molecule destruction, regulation of its targets occurs through multiple pathways, including ubiquitin-independent mechanisms.
Figures



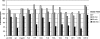


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

