Accumulation of pathological tau species and memory loss in a conditional model of tauopathy
- PMID: 17409229
- PMCID: PMC6672413
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0587-07.2007
Accumulation of pathological tau species and memory loss in a conditional model of tauopathy
Abstract
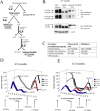
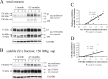
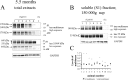
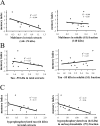
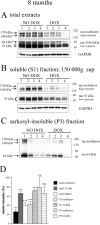
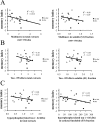
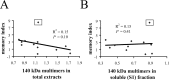
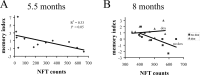
Neurofibrillary tangles (NFTs) are a pathological hallmark of Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies, but recent studies in a conditional mouse model of tauopathy (rTg4510) have suggested that NFT formation can be dissociated from memory loss and neurodegeneration. This suggests that NFTs are not the major neurotoxic tau species, at least during the early stages of pathogenesis. To identify other neurotoxic tau protein species, we performed biochemical analyses on brain tissues from the rTg4510 mouse model and then correlated the levels of these tau proteins with memory loss. We describe the identification and characterization of two forms of tau multimers (140 and 170 kDa), whose molecular weight suggests an oligomeric aggregate, that accumulate early in the pathogenic cascade in this mouse model. Similar tau multimers were detected in a second mouse model of tauopathy (JNPL3) and in tissue from patients with Alzheimer's disease and FTDP-17 (frontotemporal dementia and parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17). Moreover, levels of the tau multimers correlated consistently with memory loss at various ages in the rTg4510 mouse model. Our findings suggest that accumulation of early-stage aggregated tau species, before the formation of NFT, is associated with the development of functional deficits during the pathogenic progression of tauopathy.
Figures


References
-
- Alonso AD, Grundke-Iqbal I, Barra HS, Iqbal K. Abnormal phosphorylation of tau and the mechanism of Alzheimer neurofibrillary degeneration: sequestration of microtubule-associated proteins 1 and 2 and the disassembly of microtubules by the abnormal tau. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1997;94:298–303. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Andorfer C, Kress Y, Espinoza M, de Silva R, Tucker KL, Barde YA, Duff K, Davies P. Hyperphosphorylation and aggregation of tau in mice expressing normal human tau isoforms. J Neurochem. 2003;86:582–590. - PubMed
-
- Arriagada PV, Growdon JH, Hedley-Whyte ET, Hyman BT. Neurofibrillary tangles but not senile plaques parallel duration and severity of Alzheimer's disease. Neurology. 1992;42:631–639. - PubMed
-
- Arvanitakis Z, Witte RJ, Dickson DW, Tsuboi Y, Uitti RJ, Slowinski J, Hutton ML, Lin SC, Boeve BF, Cheshire WP, Pooley RA, Liss JM, Caviness JN, Strongosky AJ, Wszolek ZK. Clinical-pathologic study of biomarkers in FTDP-17 (PPND family with N279K tau mutation) Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2006 in press. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
