Dopamine receptor activation modulates GABA neuron migration from the basal forebrain to the cerebral cortex
- PMID: 17409246
- PMCID: PMC2711976
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5124-06.2007
Dopamine receptor activation modulates GABA neuron migration from the basal forebrain to the cerebral cortex
Abstract
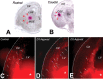
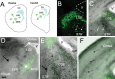
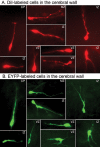
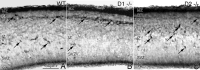
GABA neurons of the cerebral cortex and other telencephalic structures are produced in the basal forebrain and migrate to their final destinations during the embryonic period. The embryonic basal forebrain is enriched in dopamine and its receptors, creating a favorable environment for dopamine to influence GABA neuron migration. However, whether dopamine receptor activation can influence GABA neuron migration is not known. We show that dopamine D1 receptor activation promotes and D2 receptor activation decreases GABA neuron migration from the medial and caudal ganglionic eminences to the cerebral cortex in slice preparations of embryonic mouse forebrain. Slice preparations from D1 or D2 receptor knock-out mouse embryos confirm the findings. In addition, D1 receptor electroporation into cells of the basal forebrain and pharmacological activation of the receptor promote migration of the electroporated cells to the cerebral cortex. Analysis of GABA neuron numbers in the cerebral wall of the dopamine receptor knock-out mouse embryos further confirmed the effects of dopamine receptor activation on GABA neuron migration. Finally, dopamine receptor activation mobilizes striatal neuronal cytoskeleton in a manner consistent with the effects on neuronal migration. These data show that impairing the physiological balance between D1 and D2 receptors can alter GABA neuron migration from the basal forebrain to the cerebral cortex. The intimate relationship between dopamine and GABA neuron development revealed here may offer novel insights into developmental disorders such as schizophrenia, attention deficit or autism, and fetal cocaine exposure, all of which are associated with dopamine and GABA imbalance.
Figures

References
-
- Aizman O, Brismar H, Uhlen P, Zettergren E, Levey AI, Forssberg H, Greengard P, Aperia A. Anatomical and physiological evidence for D1 and D2 dopamine receptor colocalization in neostriatal neurons. Nat Neurosci. 2000;3:226–230. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SA, Eisenstat DD, Shi L, Rubenstein JLR. Interneuron migration from basal forebrain to neocortex: dependence on Dlx genes. Science. 1997;278:474–476. - PubMed
-
- Anderson SA, Marin O, Horn C, Jennings K, Rubenstein JL. Distinct cortical migrations from the medial and lateral ganglionic eminences. Development. 2001;128:353–363. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
