GABAergic control of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in relation to behavior indicative of trait anxiety and depression states
- PMID: 17409249
- PMCID: PMC2441879
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3609-06.2007
GABAergic control of adult hippocampal neurogenesis in relation to behavior indicative of trait anxiety and depression states
Abstract
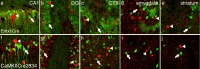
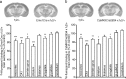
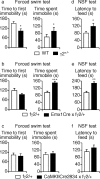
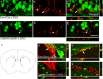
Stressful experiences in early life are known risk factors for anxiety and depressive illnesses, and they inhibit hippocampal neurogenesis and the expression of GABA(A) receptors in adulthood. Conversely, deficits in GABAergic neurotransmission and reduced neurogenesis are implicated in the etiology of pathological anxiety and diverse mood disorders. Mice that are heterozygous for the gamma2 subunit of GABA(A) receptors exhibit a modest functional deficit in mainly postsynaptic GABA(A) receptors that is associated with a behavioral, cognitive, and pharmacological phenotype indicative of heightened trait anxiety. Here we used cell type-specific and developmentally controlled inactivation of the gamma2 subunit gene to further analyze the mechanism and brain substrate underlying this phenotype. Heterozygous deletion of the gamma2 subunit induced selectively in immature neurons of the embryonic and adult forebrain resulted in reduced adult hippocampal neurogenesis associated with heightened behavioral inhibition to naturally aversive situations, including stressful situations known to be sensitive to antidepressant drug treatment. Reduced adult hippocampal neurogenesis was associated with normal cell proliferation, indicating a selective vulnerability of postmitotic immature neurons to modest functional deficits in gamma2 subunit-containing GABA(A) receptors. In contrast, a comparable forebrain-specific GABA(A) receptor deficit induced selectively in mature neurons during adolescence lacked neurogenic and behavioral consequences. These results suggest that modestly reduced GABA(A) receptor function in immature neurons of the developing and adult brain can serve as a common molecular substrate for deficits in adult neurogenesis and behavior indicative of anxious and depressive-like mood states.
Figures
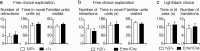

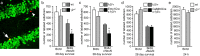
References
-
- Benson DL, Isackson PJ, Gall CM, Jones EG. Contrasting patterns in the localization of glutamic acid decarboxylase and Ca2+/calmodulin protein kinase gene expression in the rat central nervous system. Neuroscience. 1992;46:825–849. - PubMed
-
- Bergersen L, Ruiz A, Bjaalie JG, Kullmann DM, Gundersen V. GABA and GABAA receptors at hippocampal mossy fibre synapses. Eur J Neurosci. 2003;18:931–941. - PubMed
-
- Brambilla P, Perez J, Barale F, Schettini G, Soares JC. GABAergic dysfunction in mood disorders. Mol Psychiatry. 2003;8:721–737. 715. - PubMed
-
- Bremne JD, Vermetten E. Stress and development: behavioral and biological consequences. Dev Psychopathol. 2001;13:473–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
