Active Arf6 recruits ARNO/cytohesin GEFs to the PM by binding their PH domains
- PMID: 17409355
- PMCID: PMC1877112
- DOI: 10.1091/mbc.e06-11-0998
Active Arf6 recruits ARNO/cytohesin GEFs to the PM by binding their PH domains
Abstract
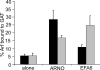
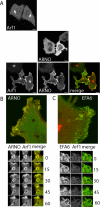
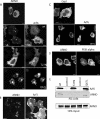
ARNO is a soluble guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) for the Arf family of GTPases. Although in biochemical assays ARNO prefers Arf1 over Arf6 as a substrate, its localization in cells at the plasma membrane (PM) suggests an interaction with Arf6. In this study, we found that ARNO activated Arf1 in HeLa and COS-7 cells resulting in the recruitment of Arf1 on to dynamic PM ruffles. By contrast, Arf6 was activated less by ARNO than EFA6, a canonical Arf6 GEF. Remarkably, Arf6 in its GTP-bound form recruited ARNO to the PM and the two proteins could be immunoprecipitated. ARNO binding to Arf6 was not mediated through the catalytic Sec7 domain, but via the pleckstrin homology (PH) domain. Active Arf6 also bound the PH domain of Grp1, another ARNO family member. This interaction was direct and required both inositol phospholipids and GTP. We propose a model of sequential Arf activation at the PM whereby Arf6-GTP recruits ARNO family GEFs for further activation of other Arf isoforms.
Figures




References
-
- Antonny B., Beraud-Dufour S., Chardin P., Chabre M. N-terminal hydrophobic residues of the G-protein ADP-ribosylation factor-1 insert into membrane phospholipids upon GDP to GTP exchange. Biochemistry. 1997;36:4675–4684. - PubMed
-
- Balla T. Inositol-lipid binding motifs: signal integrators through protein-lipid and protein-protein interactions. J. Cell Sci. 2005;118:2093–2104. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

